Last Updated:
Forex Broker is an essential factor in determining the success of your trading. Many available retail forex brokers offer their services online. Not all of them are easy to work with or suitable for your trading needs. In this guide, we have identified some important key areas you should consider when choosing the best forex broker for yourself.
We have created a little custom GTP from OpenAi. You can get a try here to find out the best Forex Broker using AI.
Top Forex Brokers You Should Know In 2024

Before indulging yourself with our ultimate guide on forex brokers, we have prepared a quick list of the best forex brokers in 2024 for your digestion.
Regulated Brokers
| Rank | Broker Name | Regulators | Maximum Leverage |
|---|---|---|---|
| #1 | XM | ASIC (Australia), CySEC (Cyprus), DFSA (United Arab Emirates), FSC (Belize) | 1:1000 |
| #2 | FP Markets | ASIC (Australia), CySEC (Cyprus) | 1:500 |
| #3 | FBS | CySEC (Cyprus), FSC (Belize) | 1:3000 |
| #4 | HFM | CySEC (Cyprus), DFSA (United Arab Emirates), FCA (United Kingdom), FSA (Seychelles), FSCA (South Africa) | 1:1000 |
| #5 | AximTrade | ASIC (Australia) | 1:3000 |
| #6 | Axiory | FSC (Belize) | 1:777 |
| #7 | Number One Capital Markets | VFSC (Vanuatu) | 1:1000 |
| #8 | PrimeXBT | ASIC (Australia) | 1:1000 |
| #9 | Rakuten Securities | ASIC (Australia), FSA (Japan), SFC (Hong Kong) | 1:400 |
| #10 | Exness | CySEC (Cyprus), FCA (United Kingdom), FSA (Seychelles), FSC (The British Virgin Islands), FSC (Mauritius), FSCA (South Africa) | 1:1000000 |
| #11 | eToro | ADGM FSRA (Abu Dhabi), ASIC (Australia), CySEC (Cyprus), FCA (United Kingdom), FSA (Seychelles) | 1:400 |
| #12 | Oanda | FSC (The British Virgin Islands) | 1:200 |
| #13 | IG | AMF (France), ASIC (Australia), DFSA (United Arab Emirates), FCA (United Kingdom), FMA (New Zealand), FSA (Japan), MAS (Singapore), NFA (United States) | 1:30 |
| #14 | IC Markets | ASIC (Australia), CySEC (Cyprus), FSA (Seychelles) | 1:1000 |
| #15 | VantageMarkets | ASIC (Australia), CIMA (Cayman Islands), FCA (United Kingdom), VFSC (Vanuatu) | 1:500 |
| #16 | Forex Capital Markets | ASIC (Australia), CySEC (Cyprus), FCA (United Kingdom), FSCA (South Africa) | 1:1000 |
| #17 | AvaTrade | ADGM FSRA (Abu Dhabi), ASIC (Australia), CBI (Ireland) , CySEC (Cyprus), FFAJ (Japan), FSA (Japan), FSC (The British Virgin Islands), FSCA (South Africa), ISA (Israel), KNF (Poland) | 1:400 |
| #18 | FOREX.com | ASIC (Australia), CIMA (Cayman Islands), FCA (United Kingdom), FSA (Japan), IIROC (Canada), MAS (Singapore), NFA (United States) | 1:200 |
| #19 | Trade Nation | ASIC (Australia), FCA (United Kingdom), SCB (Bahamas) | 1:200 |
| #20 | GO Markets | ASIC (Australia), CySEC (Cyprus), FSA (Seychelles), FSC (Mauritius) | 1:500 |
| #21 | easyMarkets | ASIC (Australia), CySEC (Cyprus), FSA (Seychelles), FSC (The British Virgin Islands) | 1:2000 |
| #22 | Pepperstone | ASIC (Australia), CySEC (Cyprus), DFSA (United Arab Emirates), FCA (United Kingdom), SCB (Bahamas) | 1:500 |
| #23 | Eightcap | ASIC (Australia), CySEC (Cyprus), FCA (United Kingdom), SCB (Bahamas) | 1:500 |
| #24 | Binary.com | FSC (The British Virgin Islands), LFSA (Malaysia), VFSC (Vanuatu) | 1:1000 |
| #25 | FXTRADING.com | ASIC (Australia), VFSC (Vanuatu) | 1:500 |
| #26 | Spreadex | FCA (United Kingdom) | 1:30 |
| #27 | ATFX | ASIC (Australia), CySEC (Cyprus), FCA (United Kingdom), FSA (Seychelles), FSC (Mauritius), JSC (Jordan), SCA (United Arab Emirates) | 1:400 |
| #28 | HYCM | CIMA (Cayman Islands), CySEC (Cyprus), DFSA (United Arab Emirates), FCA (United Kingdom) | 1:500 |
| #29 | ActivTrades | CMVM (Portugal), FCA (United Kingdom), SCB (Bahamas) | 1:400 |
| #30 | Decode Global | ASIC (Australia), VFSC (Vanuatu) | 1:500 |
| #31 | ETO Markets | ASIC (Australia), FSA (Seychelles) | 1:500 |
| #32 | Trading212 | CySEC (Cyprus), FCA (United Kingdom) | 1:30 |
| #33 | STARTRADER | ASIC (Australia), FCA (United Kingdom), FSA (Seychelles), FSCA (South Africa) | 1:500 |
| #34 | RoboForex | CySEC (Cyprus), FSC (Belize), NBRB (Belarus) | 1:2000 |
| #35 | Prospero | ASIC (Australia) | 1:400 |
| #36 | BUX Markets | CySEC (Cyprus), FCA (United Kingdom) | 1:30 |
| #37 | Squared Financial | BDF (France) , BaFin (Germany) , CNMV (Spain), CySEC (Cyprus), FSA (Seychelles) | 1:500 |
| #38 | BCR | ASIC (Australia), FSC (The British Virgin Islands) | 1:400 |
| #39 | Tier1FX | MFSA (Malta) | 1:200 |
| #40 | Fortune Prime Global | ASIC (Australia), VFSC (Vanuatu) | 1:500 |
| #41 | Quadcode Markets | ASIC (Australia), CySEC (Cyprus), SCB (Bahamas) | 1:200 |
| #42 | ThinkMarkets | ASIC (Australia), CIMA (Cayman Islands), CySEC (Cyprus), FCA (United Kingdom), FSA (Japan), FSA (Seychelles), FSC (Mauritius), FSCA (South Africa) | 1:500 |
| #43 | FxPro | CySEC (Cyprus), FCA (United Kingdom), FSC (Mauritius), FSCA (South Africa), SCB (Bahamas) | 1:200 |
| #44 | Fortrade | ASIC (Australia), CySEC (Cyprus), FCA (United Kingdom), FSC (Mauritius), IIROC (Canada), NBRB (Belarus) | 1:200 |
| #45 | TMGM | ASIC (Australia), FMA (New Zealand), VFSC (Vanuatu) | 1:30 |
| #46 | Tickmill | CySEC (Cyprus), DFSA (United Arab Emirates), FCA (United Kingdom), FSA (Seychelles), FSCA (South Africa), LFSA (Malaysia) | 1:500 |
| #47 | BDSwiss | FSA (Seychelles), FSC (Mauritius) | 1:500 |
| #48 | OctaFX | CySEC (Cyprus) | 1:500 |
| #49 | Anzo Capital | FCA (United Kingdom), FSC (Belize) | 1:1000 |
| #50 | AUS Global | ASIC (Australia), CySEC (Cyprus) | 1:500 |
| #51 | GMI | FCA (United Kingdom), FSC (Mauritius) | 1:2000 |
| #52 | IronFX | CySEC (Cyprus), FCA (United Kingdom) | 1:30 |
| #53 | INFINOX | FCA (United Kingdom), FSC (Mauritius), SCB (Bahamas) | 1:1000 |
| #54 | Trive | FSCA (South Africa), MFSA (Malta) | 1:30 |
| #55 | VT Markets | FSCA (South Africa) | 1:500 |
| #56 | JDR | ASIC (Australia), FSPR (New Zealand) | 1:400 |
| #57 | Scope Markets | CySEC (Cyprus), FSA (Seychelles), FSC (Belize) | 1:2000 |
| #58 | DCFX | BAPPEBTI (Indonesia) , FCA (United Kingdom), JFX (Indonesia), MAS (Singapore) | 1:1000 |
| #59 | FairMarkets | ASIC (Australia), FSC (Mauritius) | 1:1000 |
| #60 | NessFx | CySEC (Cyprus) | 1:500 |
| #61 | London Capital Group | FCA (United Kingdom), SCB (Bahamas) | 1:200 |
| #62 | Taurex | FCA (United Kingdom), FSA (Seychelles) | 1:1000 |
| #63 | Colmex Pro | CySEC (Cyprus) | 1:200 |
| #64 | ADS Securities | FCA (United Kingdom), SCA (United Arab Emirates) | 1:500 |
| #65 | Fusion Markets | ASIC (Australia), FSA (Seychelles), VFSC (Vanuatu) | 1:500 |
| #66 | ACY Securities | ASIC (Australia) | 1:500 |
| #67 | EBC | ASIC (Australia), FCA (United Kingdom) | 1:500 |
| #68 | nextmarkets | MFSA (Malta) | 1:30 |
| #69 | Hantec Markets | ASIC (Australia), CGSE (Hong Kong), FCA (United Kingdom), FSC (Mauritius), JSC (Jordan) | 1:1000 |
| #70 | CAPEX | ADGM FSRA (Abu Dhabi), ASF (Romania), CNMV (Spain), CySEC (Cyprus), FSA (Seychelles), FSCA (South Africa) | 1:300 |
| #71 | Dukascopy Bank | FINMA (Switzerland), FSA (Japan) | 1:200 |
| #72 | TrioMarkets | CySEC (Cyprus), FSC (Mauritius) | 1:500 |
| #73 | GBE brokers | BaFin (Germany) , CySEC (Cyprus) | 1:400 |
| #74 | AETOS Capital Group | ASIC (Australia), FCA (United Kingdom), VFSC (Vanuatu) | 1:400 |
| #75 | Xtrade | ASIC (Australia), FSC (Belize), FSCA (South Africa) | 1:400 |
| #76 | Windsor Brokers | CMA (Kenya), CySEC (Cyprus), FSA (Seychelles), FSC (Belize), FSC (The British Virgin Islands), JSC (Jordan) | 1:1000 |
| #77 | FIBO Group | BaFin (Germany) , CySEC (Cyprus), FSC (The British Virgin Islands) | 1:1000 |
| #78 | OEXN | CySEC (Cyprus), FSC (Mauritius) | 1:1000 |
| #79 | ZFX | FCA (United Kingdom), FSA (Seychelles) | 1:2000 |
| #80 | Ultima Markets | ASIC (Australia), CySEC (Cyprus), FSC (Mauritius) | 1:2000 |
| #81 | AccuIndex | CySEC (Cyprus), FSC (Mauritius) | 1:400 |
| #82 | LiteFinance | CySEC (Cyprus) | 1:1000 |
| #83 | Acetop Financial | FCA (United Kingdom) | 1:30 |
| #84 | TopFX | CySEC (Cyprus), FSA (Seychelles) | 1:1000 |
| #85 | Skilling | CySEC (Cyprus), FSA (Seychelles) | 1:1000 |
| #86 | Mitrade | ASIC (Australia), CIMA (Cayman Islands), FSC (Mauritius) | 1:200 |
| #87 | Victory International Futures | BAPPEBTI (Indonesia) , ICDX (Indonesia) | 1:100 |
| #88 | Valutrades | FCA (United Kingdom), FSA (Seychelles) | 1:500 |
| #89 | Spread Co | FCA (United Kingdom) | 1:30 |
| #90 | FXTM | CMA (Kenya), CySEC (Cyprus), FCA (United Kingdom), FSC (Mauritius), FSCA (South Africa) | 1:2000 |
| #91 | DIDIMAX | BAPPEBTI (Indonesia) , JFX (Indonesia) | 1:400 |
| #92 | TradersTrust | CySEC (Cyprus), FSA (Seychelles) | 1:3000 |
| #93 | Sky Alliance Markets | ASIC (Australia) | 1:400 |
| #94 | IEXS | ASIC (Australia), FCA (United Kingdom), FINTRAC (Canada) | 1:800 |
| #95 | PRCBroker | CySEC (Cyprus), VFSC (Vanuatu) | 1:100 |
| #96 | Land-FX | FCA (United Kingdom) | 1:2000 |
| #97 | FXORO | CNMV (Spain), CySEC (Cyprus), FSA (Seychelles) | 1:400 |
| #98 | ForexMart | FCA (United Kingdom), FSC (The British Virgin Islands) | 1:3000 |
| #99 | Darwinex | CNMV (Spain), FCA (United Kingdom) | 1:200 |
| #100 | OBR Investments | CySEC (Cyprus) | 1:400 |
| #101 | ALB | MFSA (Malta) | 1:200 |
| #102 | InterStellar Group | CySEC (Cyprus), FSA (Seychelles) | 1:500 |
| #103 | Mohican Markets | ASIC (Australia), FINTRAC (Canada), VFSC (Vanuatu) | 1:400 |
| #104 | Conotoxia | CySEC (Cyprus) | 1:300 |
| #105 | ATC Brokers | CIMA (Cayman Islands), FCA (United Kingdom) | 1:200 |
| #106 | OneRoyal | ASIC (Australia), CySEC (Cyprus), VFSC (Vanuatu) | 1:1000 |
| #107 | Capital Index | FCA (United Kingdom), SCB (Bahamas) | 1:200 |
| #108 | Merlion Global | FSC (Mauritius), SECC (Cambodia) | 1:500 |
| #109 | EC Markets | ASIC (Australia), FCA (United Kingdom), FMA (New Zealand), FSA (Seychelles), FSC (Mauritius) | 1:500 |
| #110 | FTM Brokers | NBRB (Belarus) | 1:200 |
| #111 | Oqtima | CySEC (Cyprus), FSA (Seychelles) | 1:500 |
| #112 | M4Markets | CySEC (Cyprus), DFSA (United Arab Emirates), FSA (Seychelles) | 1:5000 |
| #113 | Libertex | CySEC (Cyprus), FSC (Mauritius) | 1:999 |
| #114 | Geldex Invest | CySEC (Cyprus) | 1:100 |
| #115 | Orbex | CySEC (Cyprus), FSC (Mauritius) | 1:500 |
| #116 | Orfinex | ASIC (Australia), FSC (Mauritius), FinCEN (United States) | 1:500 |
| #117 | Investing24 | CySEC (Cyprus) | 1:500 |
| #118 | BlackBull Markets | FMA (New Zealand), FSA (Seychelles) | 1:500 |
| #119 | Trading Pro | FSCA (South Africa) | 1:2000 |
| #120 | MEX Exchange | ASIC (Australia) | 1:500 |
| #121 | 4T | FCA (United Kingdom), FSA (Seychelles) | 1:300 |
| #122 | One Financial Markets | FCA (United Kingdom), FSCA (South Africa) | 1:400 |
| #123 | Ox Securities | ASIC (Australia) | 1:500 |
| #124 | Auric International Markets | ASIC (Australia), LFSA (Malaysia) | 1:400 |
| #125 | JustMarkets | CySEC (Cyprus), FSA (Seychelles), FSC (Mauritius) | 1:3000 |
| #126 | Long Asia | ASIC (Australia), FINTRAC (Canada) | 1:500 |
| #127 | NSFX | MFSA (Malta) | 1:50 |
| #128 | XBMarkets | CySEC (Cyprus) | 1:200 |
| #129 | XtreamForex | FSC (Mauritius) | 1:1000 |
| #130 | RockGlobal | FMA (New Zealand) | 1:500 |
| #131 | Axi | ASIC (Australia), DFSA (United Arab Emirates), FCA (United Kingdom) | 1:500 |
| #132 | Global Trade Capital | FCA (United Kingdom), FSC (Mauritius), SCA (United Arab Emirates), VFSC (Vanuatu) | 1:1000 |
| #133 | TDX Global | ASIC (Australia), FinCEN (United States) | 1:500 |
| #134 | ICM | ADGM FSRA (Abu Dhabi), FCA (United Kingdom), FSC (Mauritius), FSCA (South Africa), LFSA (Malaysia) | 1:200 |
| #135 | DLS Markets | ASIC (Australia), VFSC (Vanuatu) | 1:1000 |
| #136 | National Coin Exchange | ASIC (Australia), FSA (Seychelles) | 1:1000 |
| #137 | IGM Forex | CySEC (Cyprus) | 1:400 |
| #138 | iFOREX | CySEC (Cyprus), FSC (The British Virgin Islands) | 1:400 |
| #139 | CXM Trading | FCA (United Kingdom), FSC (Mauritius) | 1:1000 |
| #140 | eurotrader | CySEC (Cyprus), FCA (United Kingdom), FSCA (South Africa) | 1:500 |
| #141 | Doto | CySEC (Cyprus), FSA (Seychelles), FSC (Mauritius), FSCA (South Africa) | 1:500 |
| #142 | Just2Trade | CySEC (Cyprus) | 1:500 |
| #143 | Markets.com | ASIC (Australia), CySEC (Cyprus), FCA (United Kingdom), FSC (The British Virgin Islands), FSCA (South Africa) | 1:300 |
| #144 | IQ Option | CySEC (Cyprus) | 1:500 |
| #145 | ForexBY | NBRB (Belarus) | 1:200 |
| #146 | LegacyFX | CySEC (Cyprus), VFSC (Vanuatu) | 1:200 |
| #147 | YaMarkets | FSC (Mauritius), VFSC (Vanuatu) | 1:1000 |
| #148 | Tradeview Markets | CIMA (Cayman Islands), LFSA (Malaysia) | 1:400 |
| #149 | RightFX | FSC (Mauritius) | 1:500 |
| #150 | MogaFX | ASIC (Australia) | 1:500 |
| #151 | Pacific Financial Derivatives | FMA (New Zealand) | 1:300 |
| #152 | Amega | FSC (Mauritius) | 1:1000 |
| #153 | TradeEU | CySEC (Cyprus) | 1:30 |
| #154 | Soho Markets | CySEC (Cyprus), FSC (Mauritius) | 1:500 |
| #155 | Phillip Nova | MAS (Singapore) | 1:20 |
| #156 | XTrend | CySEC (Cyprus) | 1:300 |
| #157 | Trust Capital | CySEC (Cyprus) | 1:400 |
| #158 | Crib Markets | FSC (Mauritius) | 1:500 |
| #159 | FX Central Clearing | CySEC (Cyprus) | 1:500 |
| #160 | T4Trade | FSA (Seychelles) | 1:1000 |
| #161 | InterTrader | FCA (United Kingdom) | 1:30 |
| #162 | Eight Plus | CySEC (Cyprus) | 1:100 |
| #163 | ATG WORLD | FSA (Seychelles) | 1:500 |
| #164 | Equiti | FSA (Seychelles) | 1:2000 |
| #165 | Ngel Partners | LFSA (Malaysia) | 1:200 |
| #166 | LeoPrime | FSA (Seychelles) | 1:1000 |
| #167 | TeraFX | FCA (United Kingdom) | 1:500 |
| #168 | IFC Markets | FSC (The British Virgin Islands) | 1:400 |
| #169 | Axon Markets | FSA (Seychelles) | 1:2000 |
| #170 | Titan FX | FSA (Seychelles), FSC (The British Virgin Islands), FSC (Mauritius), VFSC (Vanuatu) | 1:1000 |
| #171 | Goldwell Capital | ASIC (Australia), SECC (Cambodia) | 1:200 |
| #172 | Errante | CySEC (Cyprus), FSA (Seychelles) | 1:500 |
| #173 | IUX Markets | FSCA (South Africa), MISA (Comoros) | 1:3000 |
| #174 | DNA Markets | ASIC (Australia) | 1:500 |
| #175 | Forex4you | FSC (The British Virgin Islands) | 1:2000 |
| #176 | SECURCAP | FSA (Seychelles) | 1:1000 |
| #177 | Axion Trade | ASIC (Australia) | 1:500 |
| #178 | Alchemy Prime | FCA (United Kingdom) | 1:200 |
| #179 | FXCentrum | FSA (Seychelles) | 1:1000 |
| #180 | Global Femic Services | ASIC (Australia) | 1:500 |
| #181 | ZaraFX | FINTRAC (Canada), FSC (Mauritius) | 1:500 |
| #182 | OnEquity | FSA (Seychelles), FSCA (South Africa) | 1:500 |
| #183 | Rock-West | FSA (Seychelles) | 1:1000 |
| #184 | FXOpulence | ASIC (Australia) | 1:500 |
| #185 | FinPros | FSA (Seychelles) | 1:500 |
| #186 | Connext | FSA (Seychelles) | 1:1000 |
| #187 | JMI | VFSC (Vanuatu) | 1:500 |
| #188 | Market Equity | LFSA (Malaysia), VFSC (Vanuatu) | 1:500 |
| #189 | FxGrow | CySEC (Cyprus), VFSC (Vanuatu) | 1:100 |
| #190 | CMS Prime | FSC (Mauritius) | 1:500 |
| #191 | AAAFx | FSCA (South Africa) | 1:500 |
| #192 | xChief | MISA (Comoros), VFSC (Vanuatu) | 1:1000 |
| #193 | TradeWill | ASIC (Australia) | 1:500 |
| #194 | Gerchik & Co | VFSC (Vanuatu) | 1:100 |
| #195 | Venn Prime Securities | LFSA (Malaysia) | 1:100 |
| #196 | AccentForex | VFSC (Vanuatu) | 1:500 |
| #197 | Golden Brokers | LFSA (Malaysia) | 1:100 |
| #198 | Radex Markets | FSA (Seychelles) | 1:500 |
| #199 | Exclusive Markets | FSA (Seychelles) | 1:2000 |
| #200 | Main Group FX | ASIC (Australia) | 1:30 |
| #201 | ClickTrades | FSA (Seychelles) | 1:300 |
| #202 | Trade Quo | FSA (Seychelles) | 1:1000 |
| #203 | Vstar | CySEC (Cyprus), FSC (Mauritius) | 1:200 |
| #204 | ForexTB | CySEC (Cyprus) | 1:400 |
| #205 | Sway Markets | ASIC (Australia) | 1:500 |
| #206 | Monaxa | ASIC (Australia) | 1:2000 |
| #207 | DB Investing | FSA (Seychelles) | 1:1000 |
| #208 | Cerus Markets | LFSA (Malaysia) | 1:400 |
| #209 | 3angleFX | CySEC (Cyprus) | 1:30 |
| #210 | ThreeTrader | VFSC (Vanuatu) | 1:500 |
| #211 | Mugan Markets | FSCA (South Africa) | 1:500 |
| #212 | Thunder Markets | FSA (Seychelles) | 1:400 |
| #213 | Exfor | LFSA (Malaysia) | 1:500 |
| #214 | Opofinance | FSA (Seychelles) | 1:2000 |
| #215 | Juno Markets | ASIC (Australia), VFSC (Vanuatu) | 1:1000 |
| #216 | Switch Markets | ASIC (Australia) | 1:500 |
| #217 | SuperForex | FSC (Belize) | 1:2000 |
| #218 | IFX Brokers | FSCA (South Africa) | 1:1000 |
| #219 | AC FOREX | FSA (Seychelles) | 1:500 |
| #220 | TNFX | FSA (Seychelles) | 1:500 |
| #221 | Trade View | FSA (Seychelles) | 1:500 |
| #222 | CM Trading | FSA (Seychelles), FSCA (South Africa) | 1:200 |
| #223 | Garnet Trade | ASIC (Australia) | 1:500 |
| #224 | Alpho | FSA (Seychelles) | 1:500 |
| #225 | Finq | FSA (Seychelles) | 1:300 |
| #226 | SWmarkets | VFSC (Vanuatu) | 1:200 |
| #227 | AdroFx | VFSC (Vanuatu) | 1:500 |
| #228 | HonorFX | FSC (Mauritius), LFSA (Malaysia) | 1:500 |
| #229 | Axia Investments | FSA (Seychelles) | 1:400 |
| #230 | Purple Trading | CySEC (Cyprus), FCA (United Kingdom) | 1:500 |
| #231 | Kwakol Markets | ASIC (Australia), FINTRAC (Canada) | 1:1000 |
| #232 | 77markets | FSA (Seychelles) | 1:300 |
| #233 | Vida Markets | FSCA (South Africa) | 1:1000 |
| #234 | OnePro | FSC (Mauritius), FSPR (New Zealand) | 1:500 |
| #235 | 4xHub | LFSA (Malaysia) | 1:100 |
| #236 | Blueberry Markets | ASIC (Australia) | 1:500 |
| #237 | XTB | CNMV (Spain), CySEC (Cyprus), FCA (United Kingdom), FSC (Belize) | 1:30 |
| #238 | TD Markets | FSCA (South Africa) | 1:500 |
| #239 | Plus500 | ASIC (Australia), CySEC (Cyprus), DFSA (United Arab Emirates), FCA (United Kingdom), FMA (New Zealand), FSA (Seychelles), FSCA (South Africa), MAS (Singapore) | 1:300 |
| #240 | InstaForex | CySEC (Cyprus), FSC (The British Virgin Islands) | 1:1000 |
| #241 | JDFX | FSPR (New Zealand) | 1:400 |
| #242 | Invest Markets | FSC (Belize) | 1:500 |
| #243 | TOP1 Markets | ASIC (Australia) | 1:1000 |
| #244 | GeneTrade | FSC (Belize) | 1:1000 |
| #245 | FXGlobe | FSCA (South Africa), VFSC (Vanuatu) | 1:500 |
| #246 | PrimeX Brokers | FSCA (South Africa) | 1:500 |
| #247 | Capital.Com | ASIC (Australia), CySEC (Cyprus), FCA (United Kingdom), FSA (Seychelles), NBRB (Belarus), SCB (Bahamas) | 1:30 |
| #248 | FXGT.com | CySEC (Cyprus), FSA (Seychelles), FSCA (South Africa), VFSC (Vanuatu) | 1:1000 |
| #249 | Dollars Markets | FSC (Mauritius) | 1:2000 |
| #250 | HTFX | CySEC (Cyprus), FCA (United Kingdom) | 1:500 |
| #251 | FXPIG | VFSC (Vanuatu) | 1:500 |
| #252 | CMC Markets | ASIC (Australia), BaFin (Germany) , FCA (United Kingdom), FMA (New Zealand), IIROC (Canada), MAS (Singapore) | 1:30 |
| #253 | tegasFX | VFSC (Vanuatu) | 1:200 |
| #254 | GoDo CM | FSC (Mauritius), SCA (United Arab Emirates) | 1:1000 |
| #255 | FXPrimus | CySEC (Cyprus), VFSC (Vanuatu) | 1:1000 |
| #256 | YADIX | FSA (Seychelles) | 1:1000 |
| #257 | Baazex | FSA (Seychelles) | 1:400 |
| #258 | FXOpen | CySEC (Cyprus), FCA (United Kingdom) | 1:500 |
| #259 | FinmaxFX | VFSC (Vanuatu) | 1:200 |
| #260 | Crystal Ball Markets | FINTRAC (Canada) | 1:1000 |
| #261 | Admiral Markets | ASIC (Australia), CMA (Kenya), CySEC (Cyprus), FCA (United Kingdom), FSA (Seychelles), FSCA (South Africa), JSC (Jordan) | 1:500 |
| #262 | Hirose Financial | FCA (United Kingdom), FSA (Japan), LFSA (Malaysia) | 1:30 |
| #263 | MultiBank Group | ASIC (Australia), BaFin (Germany) , CIMA (Cayman Islands), CySEC (Cyprus), FMA (Austria), FSC (The British Virgin Islands), MAS (Singapore), SCA (United Arab Emirates), VFSC (Vanuatu) | 1:500 |
| #264 | LIRUNEX | AMF (France), BaFin (Germany) , CNMV (Spain), CySEC (Cyprus), LFSA (Malaysia) | 1:2000 |
| #265 | Global Markets Group | FCA (United Kingdom) | 1:100 |
| #266 | CWG Markets | FCA (United Kingdom), VFSC (Vanuatu) | 1:1000 |
| #267 | Key to Markets | CySEC (Cyprus), FCA (United Kingdom), FSC (Mauritius) | 1:500 |
| #268 | JFD Brokers | BDF (France) , BaFin (Germany) , CNMV (Spain), CySEC (Cyprus), VFSC (Vanuatu) | 1:400 |
| #269 | Cabana Capitals | FSC (Mauritius), FSCA (South Africa) | 1:500 |
| #270 | Capital Street FX | FSC (Mauritius) | 1:10000 |
| #271 | VARIANSE | FCA (United Kingdom), FSC (Mauritius), LFSA (Malaysia) | 1:500 |
| #272 | We Connect Global | CGSE (Hong Kong), FINTRAC (Canada) | 1:200 |
| #273 | INGOT Brokers | ASIC (Australia), CMA (Kenya), FSA (Seychelles), JSC (Jordan) | 1:500 |
| #274 | LION | CIMA (Cayman Islands), MAS (Singapore), SFC (Hong Kong) | 1:400 |
| #275 | CapitalXtend | FSC (Mauritius) | 1:5000 |
| #276 | Blackwell Global | FCA (United Kingdom), SCB (Bahamas), SFC (Hong Kong) | 1:200 |
| #277 | MIFX | BAPPEBTI (Indonesia) , ICDX (Indonesia), JFX (Indonesia) | 1:100 |
| #278 | AAATrade | BaFin (Germany) , CySEC (Cyprus) | 1:200 |
| #279 | Global Prime | ASIC (Australia), FSA (Seychelles), VFSC (Vanuatu) | 1:100 |
| #280 | Focus Markets | ASIC (Australia) | 1:30 |
| #281 | CPT Markets | FCA (United Kingdom), FSC (Belize), FSCA (South Africa) | 1:500 |
| #282 | NAGA | BaFin (Germany) , CNMV (Spain), CONSOB (Italy), CySEC (Cyprus) | 1:1000 |
| #283 | City Index | FCA (United Kingdom), MAS (Singapore) | 1:30 |
| #284 | Sheer Markets | CySEC (Cyprus) | 1:100 |
| #285 | FOREXimf | BAPPEBTI (Indonesia) , ICDX (Indonesia) | 1:500 |
| #286 | Doo Prime | ASIC (Australia), FCA (United Kingdom), FINTRAC (Canada), FSA (Seychelles), FSC (Mauritius), LFSA (Malaysia), VFSC (Vanuatu) | 1:1000 |
| #287 | Finex | BAPPEBTI (Indonesia) , JFX (Indonesia) | 1:500 |
| #288 | Trading.com | FCA (United Kingdom) | 1:30 |
| #289 | KCM Trade | ASIC (Australia), FSC (Mauritius) | 1:400 |
| #290 | RoboMarkets | CySEC (Cyprus) | 1:500 |
| #291 | X Global Markets | BaFin (Germany) , CONSOB (Italy), CySEC (Cyprus), VFSC (Vanuatu) | 1:200 |
| #292 | IMS Markets | CySEC (Cyprus) | 1:30 |
| #293 | MagnetFX | BAPPEBTI (Indonesia) , ICDX (Indonesia) | 1:400 |
| #294 | Fxview | CySEC (Cyprus), FSCA (South Africa) | 1:500 |
| #295 | Magic Compass | CySEC (Cyprus) | 1:20 |
| #296 | Moneta Markets | CIMA (Cayman Islands) | 1:500 |
| #297 | Pacific Union | CySEC (Cyprus), FSA (Seychelles) | 1:1000 |
| #298 | Afterprime | FSA (Seychelles) | 1:200 |
| #299 | MACRO MARKETS | ASIC (Australia), FSA (Seychelles) | 1:500 |
| #300 | Agrodana Futures | BAPPEBTI (Indonesia) | 1:100 |
| #301 | Woxa | FSC (Mauritius) | 1:400 |
| #302 | Sôegee Futures | BAPPEBTI (Indonesia) | 1:400 |
| #303 | FXPN | NBRB (Belarus) | 1:200 |
| #304 | FXChoice | FSC (Belize) | 1:1000 |
| #305 | ForexClub | NBRB (Belarus) | 1:1000 |
| #306 | Java | BAPPEBTI (Indonesia) , ICDX (Indonesia), JFX (Indonesia) | 1:200 |
| #307 | Vatee | ASIC (Australia), VFSC (Vanuatu) | 1:500 |
| #308 | Maxain | LFSA (Malaysia) | 1:1000 |
| #309 | Asiapro | BAPPEBTI (Indonesia) , ICDX (Indonesia) | 1:500 |
| #310 | TIO Markets | FCA (United Kingdom) | 1:1000 |
| #311 | XS | ASIC (Australia), CySEC (Cyprus), FSA (Seychelles) | 1:500 |
| #312 | Handal Semesta Berjangka | BAPPEBTI (Indonesia) , ICDX (Indonesia) | 1:400 |
| #313 | Banxso | CySEC (Cyprus) | 1:600 |
| #314 | Credit Financier Invest | BDL (Lebanon), CySEC (Cyprus), DFSA (United Arab Emirates), FCA (United Kingdom), FSA (Seychelles), FSC (Mauritius), JSC (Jordan), SCA (United Arab Emirates), VFSC (Vanuatu) | 1:500 |
| #315 | Baxia Markets | FSA (Seychelles), SCB (Bahamas) | 1:2000 |
| #316 | ORBI Trade | FSA (Seychelles) | 1:1000 |
| #317 | GWG | CySEC (Cyprus) | 1:200 |
| #318 | VIBHS | FCA (United Kingdom) | 1:30 |
| #319 | Octa | BAPPEBTI (Indonesia) , ICDX (Indonesia) | 1:500 |
| #320 | FINANSERO | CySEC (Cyprus) | 1:200 |
| #321 | TRADE.COM | CNMV (Spain), CONSOB (Italy), CySEC (Cyprus), FINRA (United States), FSC (Mauritius) | 1:300 |
| #322 | Antos Pinnacles | LFSA (Malaysia) | 1:200 |
| #323 | Axiance | FSA (Seychelles) | 1:500 |
| #324 | BelFX | FSC (Belize) | 1:500 |
| #325 | One Global Market | FCA (United Kingdom) | 1:300 |
| #326 | Capitalix | FSA (Seychelles) | 1:200 |
| #327 | Excent Capital | FSA (Seychelles) | 1:100 |
| #328 | Modmount | FSA (Seychelles) | 1:400 |
| #329 | Easy Trading Online | ASIC (Australia) | 1:500 |
| #330 | CDO Markets | VFSC (Vanuatu) | 1:500 |
| #331 | ArgoTrade | FSA (Seychelles) | 1:300 |
| #332 | Evest | VFSC (Vanuatu) | 1:400 |
| #333 | Weltrade | FSCA (South Africa) | 1:1000 |
| #334 | Headway | FSCA (South Africa) | 1:1000000 |
| #335 | Gulf Brokers | FSA (Seychelles) | 1:500 |
| #336 | Direct Trading Technologies | SCA (United Arab Emirates), VFSC (Vanuatu) | 1:200 |
| #337 | Esperio | NFA (United States) | 1:1000 |
| #338 | ForexVox | FSA (Seychelles) | 1:500 |
| #339 | Nation FX | ASIC (Australia) | 1:300 |
| #340 | INZO | FSA (Seychelles), MISA (Comoros) | 1:500 |
| #341 | QRSfx | ASIC (Australia), MISA (Comoros) | 1:500 |
| #342 | Sterling Gent Trading | FSC (The British Virgin Islands) | 1:100 |
| #343 | PatronFX | CySEC (Cyprus) | 1:400 |
| #344 | Viverno | CySEC (Cyprus) | 1:30 |
| #345 | OffersFX | CySEC (Cyprus) | 1:30 |
| #346 | Swissquote | CySEC (Cyprus), DFSA (United Arab Emirates), FCA (United Kingdom), FINMA (Switzerland), MAS (Singapore), MFSA (Malta), SFC (Hong Kong) | 1:400 |
| #347 | FXlift | CySEC (Cyprus) | 1:1000 |
| #348 | Supreme FX | FSA (Seychelles) | 1:500 |
| #349 | Blue Suisse | MFSA (Malta) | 1:30 |
| #350 | Financial Trading Dimensions | FSC (The British Virgin Islands) | 1:100 |
| #351 | Klips | CySEC (Cyprus), FSCA (South Africa) | 1:30 |
| #352 | Victory International Futures | BAPPEBTI (Indonesia) , ICDX (Indonesia) | 1:100 |
| #353 | GOFX | FSA (Seychelles) | 1:3000 |
| #354 | Bold Prime | ASIC (Australia) | 1:2000 |
| #355 | Dream Begin Global Markets | ASIC (Australia), FCA (United Kingdom), FSCA (South Africa) | 1:500 |
| #356 | CA Markets | ASIC (Australia), FSPR (New Zealand), VFSC (Vanuatu) | 1:500 |
| #357 | XB Prime | FSA (Seychelles) | 1:500 |
| #358 | EPFX | ASIC (Australia), FSCA (South Africa) | 1:500 |
Brokers Requiring Additional Regulation
| Broker Name | Maximum Leverage |
|---|---|
| Olymp Trade | 1:500 |
| MBFX | 1:500 |
| Ivision Market | 1:1000 |
| Pocket Option | 1:1000 |
| Grand Capital | 1:500 |
| Fresh Forex | 1:2000 |
| WINGO | 1:400 |
| NOZAX | 1:500 |
| LYNX | 1:40 |
| ePlanet Brokers | 1:500 |
| KVB | 1:1000 |
| Finowiz | 1:500 |
| Murrentrade | 1:500 |
| STP Trading | 1:200 |
| LDN Global Markets | 1:500 |
| Orbit FX | 1:200 |
How To Choose A Good Forex Broker

Table of Contents
A good forex broker does not have to score 10/10 for all the criteria we have in this comprehensive guide. It is certainly great enough if it can cater to your overall money management and trading styles. Every trader is unique, hence each forex broker might be suitable for different traders.
Here we break down the criteria into a few crucial parts:
- Fees and Trading Cost
- Security and Regulation
- Broker Types
- Trading Platforms and Tools
- Deposit and Withdrawal
- Account Opening
- Markets and Products
- Education
- Customer Service
- Research
- Forex Promotions and Bonuses
- Supported Trading Styles
1. Fees and Trading Cost

It is crucial to keep the overall trading cost low because it is in line with the single goal of trading: generating profit. Hence, knowing how those costs actually incur is of utmost importance for savvy traders.
Forex broker imposes broker fees to its clients in exchange for the services it provides. It is also one of the ways a forex broker covers its operation costs and gains its business income.
However, forex is also known as a zero-sum game; one man’s gain is another man’s loss. Broker fees have a direct impact on the overall trader’s performance. It will influence trading profitability in the long run especially if you are constantly trading in a big volume. Naturally, broker fees become a considerable cost for you. It is hence a factor we do not want to neglect when it comes to choosing a forex broker.
In our discovery, broker fees can be segmented into 2 main categories: Trading fees and Non-Trading Fees.
Trading Fees
Trading fees happen when you trade. They can be the commissions, spreads, and swaps (weekly commission for Islamic accounts).
It can be quite tricky when it comes to commission and spread. We have seen many models of commission and spread that are available with the forex brokers. Here are some of them:
- Higher spread + zero commission
- Lower spread + fixed commission per trade
- Zero spread + variable commission based on trade volume.
Commission
Commission usually is charged whenever a trader opens a position or closes a position. It means for a complete trade (open and close), a trader will be charged twice for the commission. The commission can be either fixed or based on the trading volume.
Every broker has its own terms and conditions when it comes to commission. In most cases, there will be no commission when the main cost of the trading comes from a spread.
Spread
In the forex market, we always see there are 2 different prices for each currency pair. In the following example, we are looking at the price difference of USDJPY.
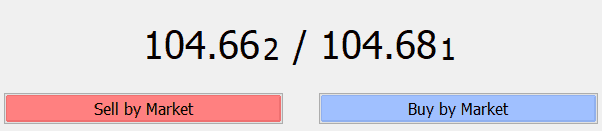
104.66 is the bid-price and 104.68 is the ask-price. Spread is simply the difference between the bid-price and the ask-price. In our case, the spread is 2 pips.
The cost of the spread is calculated in the following formula:
Spread x Traded Volume x Value of the Pip/Lot

We use the same example of USDJPY. The spread is 2 pips. Let’s say we traded 1 lot size and the value of the pip/lot is $9.
So the cost of the spread is 2 pips x $9 = $18.
Unlike commission, spread cost is only charged once per trade. It happens when the trade is opened and traders pay it when the trade is closed.
In other words, when traders open a trade with spread, the trade will have an initial loss. It is the traders’ duty to overcome the initial loss and make a profit.
Swap/Overnight Rate
Swaps are also known as the overnight rate, margin rate, financing rate, rollover rate, and funding rate.
Swap occurs when you hold an open position overnight or precisely through the cut-off time. The usual cut-off time is 5 pm ET but different brokers might have a different cut-off time. It means if you open a position at 4:21 pm ET and close it at 5:01 pm ET, a swap happens. Whatever positions that you hold through 5 pm ET are considered overnight.
When that happens, you will either be charged or paid an interest depending on the interest rates of the two currencies and the admin fees imposed by the forex broker. We call this interest a swap. There are two types of swap, namely swap long (holding a long position overnight) and swap short (holding a short position overnight).
Swap Calculation Formula
The formula of swap is as the following:
Swap = (Contract Size x (Interest Rate Difference – Admin Fee)/100) x Price/Days in A Year
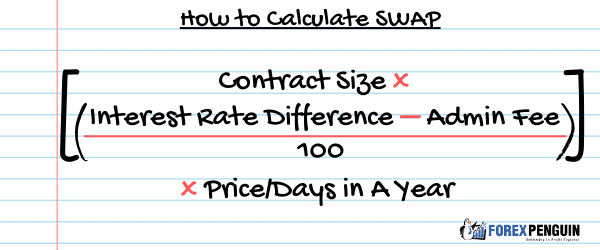
Let’s look closely at the variables of this formula.
Swap Formula Variables
Contract Size: If we are trading 1 standard lot of EUR/USD, the contract size here will be 100,000 In forex, 1 standard lot is equal to 100,000 units of the base currency and it is the same for any currency pair. The base currency is the first currency that appears in the currency pair. For example, AUD/USD, the base currency is AUD. Another example, if we open 0.1 lot of GBP/USD, then our contract size is 10,000 GBP.
Interest Rate Difference: It is the interest rate difference between the two currencies in a currency pair. In our calculation, the interest rate difference depends on whether it is a short or long trade. For example, if we buy(long) EUR/USD, the interest rate difference = interest rate of the base currency – interest rate of the quote currency (EUR interest rate – USD interest rate). In the opposite situation, if we sell(short) EUR/USD, the interest rate difference = interest rate of the quote currency – interest rate of the base currency (USD interest rate – EUR interest rate).

Admin fee: It is also called the broker markup. In the normal case, it is a predetermined fee that the broker sets. The idea behind the admin fee is that the forex broker charges an interest rate for lending you money to trade forex. It is basically the interest rate charged on the margin loans. With the leverage offered by the forex brokers, we are trading on the borrowed money. For every borrowed money, we need to pay an overnight interest.
Price: Current price when the swap occurs.
Days in a year: 365 days or 366 days.
Sometimes, traders can even earn an overnight interest instead of paying one.
In this formula, if we get a positive swap, it means we will be paid an overnight interest. However, if the swap is negative, we will pay the interest.
Nevertheless, in the current market, positive overnight rates rarely happen.
Let’s do some calculations.
Swap Calculation Example
Example 1:
Ahmad opens a long position of GBP/USD for 1 standard lot and holds it through 5 pm ET.
The current interest rate of the Bank of England (UK) is 0.10% and the Federal Reserve (US) is 0.25%.
By longing GBP/USD, Ahmad is buying 100,000 GBP (base currency) and earn interest at the rate of 0.10%. At the same time, he is also selling USD (the quote currency), borrowing at a rate of 0.25%. The admin fee of the forex broker is 0.25%.
The current price of the GBP/USD when the swap occurs is 1.2500.
From the swap formula above, we need to find out what are the variables involved.
- Contract Size: 100,000 GBP (1 standard lot)
- Interest Rate Difference: Interest rate of base currency – interest rate of quote currency. 0.1% – 0.25% = -0.15%
- Admin Fee: 0.25%
- Price: 1.2500
- Days in a year: 365
So, his swap long will be as the following:
Swap Long = (100,000 x (-0.15 – 0.25)/100)) x 1.2500 / 365 = -1.37 USD
If he shorts the position instead, the swap short is as the following:
Swap Short = (100,000 x ((0.25 – 0.10) – 0.25)/100) x 1.2500 / 365 = -0.34 USD
In both calculations, we have a negative swap. This indicates that Ahmad will have to pay the interest for both instances (long or short).
Triple Swap Wednesday
There is one more thing that we should be aware of: the triple swap Wednesday (also known as weekend swap). For every trade that is carried over from Wednesday to Thursday, it is counted as 3 nights swap interest. It is an industry-standard because of the T+2 settlement. In our example of Ahmad, if he opens a long position on Wednesday and lets it roll over to Thursday, then he would have paid 1.37 USD x 3 = 4.11 USD.
Swap is often an overlooked fee in forex trading. The cost might not occur if you are a day trader or a scalper. However, for swing traders and position traders, the swap is not something that can be neglected.
Swap Free Islamic Account
In recent years, forex brokers have created a new type of forex account that we call “Swap-Free Account” or “Islamic Account”. As the name suggests, this type of account does not have a swap element in it. The existence of this kind of account is due to the fact that Sharia laws (Islamic laws) prohibit Muslims from taking or giving any sort of interest.
In general, nobody is able to check your religious faith. That means anyone can open an Islamic account. Depending on the brokers, Islamic accounts might only be available for certain countries.
Islamic account holders may enjoy the swap-free trading environment with certain restrictions such as lower leverage, higher minimum deposit requirement, fees for holding the trading position over a certain period of time.
Nevertheless, some brokers might even charge a weekly commission for the Islamic account. In most cases before applying for a swap-free account, it is wise to consult the forex broker for the terms and conditions for this type of forex account.
Trading Fees Recap
So far we know that trading fees occur when we trade and there are 3 things that matter in the trading fees: commission, spread, and swap. Before signing up for any broker, we should find out the trading fees and factor them into our trading cost.

Conclusion: As a rule of thumb, the brokers that offer zero commission, low spread, and swap-free accounts are more preferable.
Non-Trading Fees
Non-trading fees are related to the trading account such as deposit/withdrawal fees, inactivity fees, data feeds cost and conversion fees. These fees should not be ignored because they are significant in the long run. It impacts the profitability of your trading.
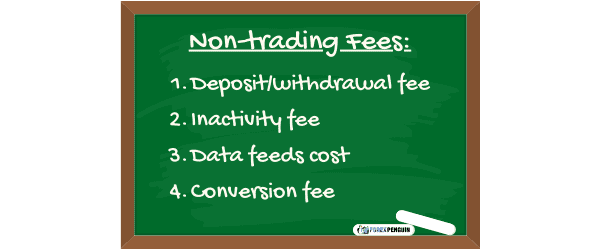
Since some of these costs are inevitable, it is good to know what is in play here.
Deposit/Withdrawal Fees
Funding a trading account is not without cost. The forex brokers sometimes will charge certain fees to cover the costs incurred with the deposit. Likewise, withdrawal has its own cost as well. The costs appear because of the transaction fees by the payment processors such as banks and digital wallets.
From our experience, normally a forex broker will absorb the deposit fees in order to encourage the traders to deposit. Similarly, a forex broker might charge some withdrawal fees to discourage the withdrawal.
Inactivity Fees
Inactivity refers to the dormant account. Some brokers might charge their clients when they are inactive for a certain period of time. Although it is not very uncommon, forex brokers could use these fees to encourage their clients to remain active.
Before committing to any broker, it is better to check with the broker whether it has such a practice.
Data Feeds Costs
Data feeds help traders to see what is going on in the market. Basically, it gives the winning edge to the traders. It is normally charged monthly and the cost can be very different depending on the quality of the feeds.
It is up to traders whether they need the data feeds to help in their trading decision.
Conversion Fees
In some cases, the base account currency is different from the funding source. Let’s say we have opened a USD base account with a forex broker but our funding source is from a European bank, which transferred the money in EUR. In such a case, the forex broker will convert the EUR it received into USD. This is where the conversion fees occur.
On other hand, when we want to withdraw our money from the USD base account back to our European bank, the USD will be converted to EUR before the withdrawal can take place. Again, we have to pay the conversion fees.
Non-Trading Fees Recap
As we discussed above, non-trading fees can contribute significantly to the cost of trading. There are many forex brokers that offer zero deposit commission, low withdrawal fees, and no inactivity fees.
For the data feeds cost, it is really up to you whether it is worth your money. If the data is helping you to make a better trading decision, then it is good to subscribe to it.
As for the conversion fees, it is recommended that you make sure the base account currency is the same as our funding currency to avoid the conversion fees.
Conclusion: Non-trading fees are not negligible and with simple research, you can find the forex brokers that are offering competitive non-trading fees.
2. Security and Regulation

Should you choose a regulated forex broker? The simple answer is yes. A regulated broker can provide a better protection shield to the traders’ money. In this section, we will look into the following details:
- The reasons for forex regulation
- The tasks of the forex regulators
- The main forex regulators in different countries
The Reasons for Forex Regulation
As of the time of writing, the forex market has a daily turnover of 6.6 trillion dollars. With such an enormous amount of money involved, it attracts a lot of scammers and white-collar criminals. These fraudsters’ sole purpose is to cart away traders’ money by illegal means. They hide behind the face of the forex brokers and make a profit by scamming the traders.
Without the right regulation, the wrongdoing of the forex brokers will just go unpunished. The common frauds and unethical practices of the forex brokers are the following:
- Ponzi schemes that promise unrealistic returns
- Churning of traders’ accounts to generate commission
- Selling of illegal software that promises great profits
- Lack of transparency in the cost of trading
- Customer complaints go unheeded
- Unethical solicitation targeting vulnerable groups such as the elderly, uneducated, and low-income individuals
- Trading against the clients
- Offering unlicensed managed accounts
- Manipulation of market pricing
- Providing high leverage trading that usually results in the loss of fund
- Practicing stop hunting
- Suggesting improper trading methods to clients.
- Giving incorrect information or misleading statements.
- Providing incentives or disincentives to encourage fund deposits and discourage fund withdrawals.

The list goes on and on. These are only some of the infamous common practices by the unregulated brokers.
Hence, the regulators are important to ensure fair play in the forex industry.
The Tasks of the Forex Regulators
In essence, the main goal of the forex regulators is to provide the check and balance in the forex market. Their tasks are the following:
- Providing financial licensing to the qualified brokers
- Monitoring the compliance of the forex brokers
- Enforcing penalty to the wrong-doing brokers
Financial Licensing
Before getting a regulated status, a forex broker needs to fulfill certain criteria set by the regulatory body. Here are some of the common requirements:
- Maximum leverage allowed
- Segregated client funds
- Negative balance protection
- Restriction of incentives
- Minimum operating capital
- Client compensation fund
- Periodical financial audit report
- Minimum initial share capital
- Restriction of hedging for traders
- A local representative office
- Fair customer conduct
There are many more terms and conditions set by the regulators. However, regulators in different parts of the world are not created equally. Every regulator has its own different rules and requirements.
Upon the fulfillment of the criteria, a financial license will be issued by the particular regulator.
Compliances Monitoring
From time to time, the regulated forex brokers are required to submit their 3rd party audited financial report to the regulator. Besides that, the trading data of their clients are subject to monitoring as well. This is to ensure the forex brokers adhere strictly to the standard set by the financial watchdogs.
Some regulators, ASIC for example, releases enforcement update every 6 months to inform the public about what they have done in the last 6 months. These reports are accessible to the public via their website.
Penalty Enforcement
If any of the regulated brokers do not comply with the rules and regulations, their regulators can take action against these brokers. Some of the known penalties are as the following:
- Reparation to the victims
- Warning
- License Suspended
- License Revoked
- Blacklisted
- Company dissolution
- Website is taken down
- Asset frozen
- Fined
- Sanction
- Banned from all investing activities
- Civil penalties
With the strong enforcement of the penalty, the regulated brokers are far safer to choose.
Conclusion: It is a recommended practice to choose a regulated broker before you decide to put your money on the line.
3. Broker Types

We have discussed the costs associated with trading forex, and gone over what you need to know about security and regulation. Now, let’s talk about the different types of forex brokers.
Forex brokers can be split into two categories. These are dealing desk brokers and no dealing desk brokers. Let’s talk about each in turn.
What are Dealing Desk Brokers?
Dealing desk brokers are also known as “market makers.” You will sometimes see “dealing desk” abbreviated simply as “DD.”
What distinguishes a dealing desk broker from a no dealing desk broker is that a DD broker takes the opposing side of your trade when necessary.
Indeed, by doing so, they make a market where there was not one before, thus why we call them “market makers.”
How do Dealing Desk Brokers work?
Here is what takes place behind the scenes when you place a trade with a dealing desk broker:
- You place an order to buy or sell a currency pair or other asset.
- If there is another client available placing the opposite order, you can be matched with each other. That client will take the other side of your trade.
- If the broker cannot find a match with another client, they can turn to a liquidity provider to take the other end of your trade.
- If they cannot get a liquidity provider to take the other side of your trade, they ensure you can trade anyway by trading against you themselves.
Hypothetically, that is possible, but it is unlikely to be an issue if you are dealing with a reputable site that manages its own risk effectively.
A solid DD broker has you trading against other clients and independent liquidity providers as much as possible.
That means they are not usually trading against their clients. So, even if their clients typically win, the broker does not typically lose as a result.
DD brokers offer fixed spreads for trades. That is how they profit regardless of whether their clients win or lose.
DD brokers are not “better” or “worse” than no dealing desk brokers. You will need to choose which type to use based on your needs and priorities. But knowing their basic pros and cons may help.
Pros of DD brokers:
- There will always be someone available to take the other end of your trade. Even if a matching client cannot be found, the dealing desk broker will use a liquidity provider or take the other end of the trade.
- Spreads are fixed. If you trade a lot during volatile times, working with a broker that maintains fixed spreads could feasibly save you a lot of money.
- Even though the rates you see listed by your DD broker are not the interbank market rates, they should be equivalent or nearly so.
Cons of DD brokers:
- Sometimes there may be more of a delay than you would get through a no dealing desk broker. Why? DD brokers manually fill orders. That means when a lot of orders are coming in, it can take more time for the broker to fill them all. So, that is a drawback during volatile times.
Summary: Dealing desk brokers, or “market makers,” offer fixed spreads and will take the opposing side of a trade if they are unable to find a match with another client or an independent liquidity provider.
What are No Dealing Desk Brokers?
Dealing desk brokers can be contrasted with no dealing desk (NDD) brokers. There are two types of no dealing desk brokers: straight-through processing (STP) and electronic communication network (ECN).

Don’t worry. This sounds complicated, but it really isn’t. We will break it down for you below.
As we explained previously, a dealing desk broker is one that sometimes takes the other side of client orders.
By contrast, no dealing desk brokers do not do that. All they do is connect you to a client or company that is taking the opposing side of your trade.
That could be another individual retail trader like you, or it might be a broker, hedge fund, bank, or mutual fund.
STP Brokers
If you go with an NDD STP broker, the broker will check quotes from a number of different liquidity providers in order to find the most competitive price for you.
The broker will then route your order to that provider, charging you a small markup for the legwork involved in finding you the best price.
Take note that you will not see the list with all the different prices in it.
Owing to the fact that the spreads of the broker are dependent on the spreads of the liquidity providers, they are variable in nature, which is a major difference from a regular dealing desk broker.
Note that while you will usually see STP brokers referred to as no dealing desk brokers, they do sometimes take the opposite side of trades.
Unlike regular dealing desk brokers though, they do not manually fill orders. They use an automatic system for it.
That is why they are called “straight-through processing” brokers.
Because they may combine aspects of the dealing desk and no dealing desk models, they might be more accurately considered to be a cross between the two, rather than strictly a type of NDD broker.
Pros of STP Brokers:
- While there is a small markup fee, there are no commissions on trades.
- The STP broker does the work for you of searching for the most competitive price at which to fill your order.
- Because orders are filled automatically, not manually, there are fewer delays.
- Spreads may be variable (but sometimes you will see fixed spreads too). This may be a plus for you if you do a lot of trading during times with lower volatility. Otherwise, it might be a drawback.
Cons of STP Brokers:
- STP brokers are not considered quite as transparent as ECN brokers, who may also have more competitive spreads.
- Variable spreads may be a disadvantage if you are a high-volatility trader.
Summary: An STP broker is classified as a no dealing desk broker, but combines aspects of DD and NDD brokers. They offer fast, automatic execution and both variable and fixed spreads. You will have to pay a small markup on your trades.
ECN Brokers
So, now you know what an STP broker is. But what is an ECN broker?
This type of NDD broker is one that matches you with liquidity providers, banks, other brokers, and other institutions.
But unlike with a regular STP broker, this type of broker displays full transparent price information.
As with STP brokers, ECN brokers fill orders automatically, not manually, for rapid execution.
ECN brokers do not trade against their clients. They simply serve as a bridge between parties.
Pros of ECN brokers:
- As with STP brokers, ECN brokers offer variable spreads. While this may be a drawback during times of high volatility, if you trade a lot during low volatility times, you might save money over fixed spreads.
- The ECN fills orders automatically rather than manually, allowing for fast execution.
- The wide range of ECN participants allows for competitive pricing and spreads.
- With ECN trading, the broker never trades against you. If you have concerns about conflicts of interest with other types of brokers, you may feel more secure trading with an ECN broker.
- ECN trading is always open, 24/7.
- You can see Depth of Market (DOM) with this type of broker. What is the Depth of Market? It is the same thing as an Order Book. It displays all the orders at various prices. That level of transparency is the highest you will find.
Cons of ECN brokers:
- An ECN broker operates with higher overhead than other types of forex brokers. So, on top of the spread, you will need to pay a commission on each of your trades. The commission will be fixed.
- You might not be able to trade with this type of broker with small account size. The minimum deposit required tends to exceed that for other types of brokers.
- There might be times you cannot trade because no one is available to trade against you. Needless to say, this can be very frustrating if you miss out on a great opportunity.
Summary: ECN brokers are NDD brokers that never trade against their clients. They fill orders automatically with variable spreads and display Depth of Market for superior transparency. They do charge commissions.
Which Broker Types to choose?
So, with respect to all the pros and cons we have talked about, here are some questions you should ask yourself when you are deciding what type of forex broker to use:
- How much money do I have to deposit? How large an account am I ready to trade with?
- During what hours do I want to be able to trade?
- How important is transparency to me? Do I want to be able to view Depth of Market?
- Will I be doing a lot of trading during high volatility times? What is most important to me, fixed spreads or fast execution?
- What am I comfortable paying in terms of spreads, markups, and commissions?
- Is it important to me that my broker never take the opposing side of my trades?
Based on your answers to these questions, you can choose the type of forex broker that is right for you.
Remember, you can also sign up with more than one FX broker. That way, you have more options and flexibility. One broker might serve you better during high volatility times, and another during low volatility times. Read on to the next section to learn about trading platforms and tools.
4. Trading Platforms and Tools

We’ve just discussed the different types of forex brokers you might encounter. Now let’s talk about trading platforms and tools.
What is a Forex Trading Platform?
A forex trading platform is a software program you can use to place trades.
Sometimes novice investors confuse trading platforms and brokers. As we have discussed, a broker is an entity that facilitates your trades.
But the platform is the actual software you interact with when you place your orders.
Some brokers offer proprietary trading platforms. But most also allow you to trade through open platforms. These are platforms that many different brokers use.
In some cases, you might decide to use one of these open platforms for trading even if there is also a proprietary platform offered by your broker.
It all comes down to what features you need.
What Should You Look For in a Quality Forex Trading Platform?
Here are some features that are important in a high-quality forex trading platform:
- Compatibility. The platform you choose must be compatible with your operating system and device as well as your broker.
- Trade Execution: A good trading platform should execute your orders rapidly with minimal slippage. A variety of different types of orders should be available. The ability to set alerts may also be important, depending on your system.
- Analytical Tools: Trading platforms may offer analytical tools that help you monitor your progress. Analytical tools may also refer to indicators and drawing tools (see below).
- Charting: Choose a platform that allows you to chart the currency pairs you want and the timeframes you need. Indicators and drawing tools can help you to establish context and identify setups that fit within your trading methods. Some platforms even let you load in custom indicators. For backtesting purposes, also look for platforms that let you scroll back through significant historical data so you can test your system over a longer time period.
- Expert Advisor/Robot Trading: Want to automate aspects of your forex trading? Pick a platform that lets you use the expert advisors or robots of your choice.
- Forex News: A quality trading platform may include a dedicated news feed to help you trade.
- Community: Social trading features allow you to collaborate with other investors for success.

Please note that these are just a few of the most important features to consider when evaluating different trading platforms.
Depending on your specific strategies, there may be other features that are imperative for your needs.
Top Recommended Forex Trading Platforms
Now that you know some of the key features to look for when comparing trading platforms, let’s go ahead and discuss some of the most prominent open trading platforms for forex.
MetaTrader 4
If there is one third-party forex trading platform that you have heard of, it is probably MetaTrader 4 (MT4). This platform from MetaQuotes Software has been around since 2005, making it one of the first big open platforms for FX traders.
The software is compatible with Android and iOS smartphones as well as Windows, Mac OS, and Linux desktop and laptop systems. You can download the program or trade on your browser.
- Trade Execution: MT4 has a solid reputation for fast trade execution.
- Analytical Tools and charting: MT4 charts are highly customizable to your needs for a wide range of currency pairs. Numerous indicators are available, and you can load in custom indicators too.
- Expert Advisor/Robot Trading: You can both use Expert Advisors and create your own.
- Forex News: Articles are available through the MT4 community.
- Community: There is a dedicated community for MT4 which gives you access to news, a forum, signals, jobs, and more.
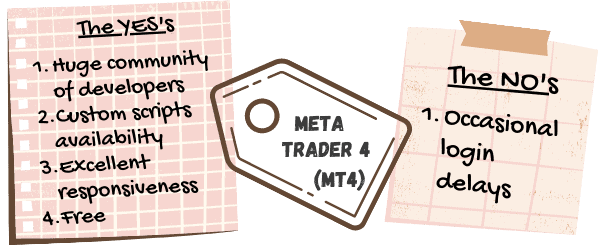
Advantages
A massive community of developers, a huge library of custom scripts, and excellent responsiveness all combine to make this one of the best trading platforms out there. Oh, and did we mention it won’t cost you a dime?
Disadvantages
It is hard to name a lot of drawbacks for MT4, but sometimes there can be delays while trying to log in.
MetaTrader 5
The follow-up to MetaTrader 4 is MetaTrader 5, which came out in 2010. Normally with software, the newest version of a program is the one most people use, but that never happened with MT5. The majority of brokers stuck with MetaTrader 4, and most traders continue to use MT4 as well a decade later.
The main reason for this is that MT5 simply has a different focus than MT4. MetaTrader 4 was built for FX specifically. MT5, on the other hand, features futures, stocks, and other assets.
- Trade Execution: Naturally, MetaTrader 5 features rapid execution just as MetaTrader 4 does.
- Analytical Tools and charting: Charting is similar for both programs, but there are 21 timeframes on MT5 versus the 9 timeframes on MT4. There are a few more built-in indicators in MT5 as well, but as you can use thousands of indicators in either program, this isn’t a big difference. If you are going to be doing any programming, you may actually find the MQL4 language for MT4 easier to grasp than the MQL5 language for MT5.
- Expert Advisor/Robot Trading: Like MT4, MT5 supports a huge range of Expert Advisors.
- Forex News: MT5 features a built-in Economic Calendar.
- Community: Like MT4, MT5 has an active community dedicated to signals, articles, and more.
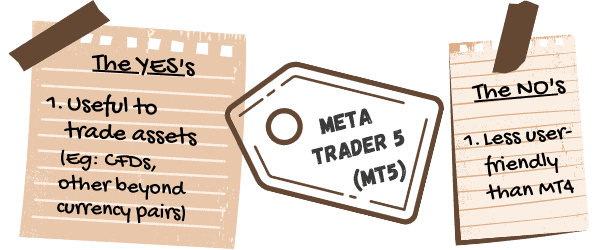
Advantages
MetaTrader 5 may be ideal if you are wanting to trade assets such as CFDs and others beyond currency pairs.
Disadvantages
MT5 is not as user-friendly as MT4, which is why many people don’t get into using it unless they need it to trade other assets. It makes more sense for the majority of forex traders to stick with MT4.
cTrader
The same year that MT5 came out, cTrader showed up from a company called Spotware. It is compatible with Windows operating systems as far back as Windows 7 as well as Android and iOS systems. There also is a web version.
- Trade Execution: Trades execute quickly and reliably through cTrader.
- Analytical Tools and charting: cTrader Analyze can help you examine your performance. Custom indicators are available in the desktop version of cTrader.
- Expert Advisor/Robot Trading: You can automate trading using cBots through cTrader Automate. The code editor also allows you to develop custom cBots and indicators yourself.
- Forex News: It is possible to integrate the FXStreet economic calendar.
- Community: Community resources and support for cTrader are minimal compared to what is available for MT4 and MT5.
Advantages
cTrader stands out with respect to ease-of-use, even compared to MT4. Also, it has come a long way since its original introduction and has many more features than it boasted when it was new.
Disadvantages
Even though auto-trading and custom indicators are supported by cTrader, the selection is much larger through MT4, and the support is more substantial.
NinjaTrader
Another of the oldest third-party trading platforms for forex is NinjaTrader. Since 2004, investors have been using this software for not just forex trading, but also for other assets like futures and stocks. Unlike some other platforms, NinjaTrader relies on other providers for market data rather than functioning as a provider itself.
- Trade Execution: This platform has a longstanding reputation for fast and reliable execution of trades.
- Analytical Tools and charting: There are thousands of indicators and apps available for NinjaTrader.
- Expert Advisor/Robot Trading: You can use more than a hundred automated strategies with this platform.
- Forex News: NinjaTrader maintains an active blog with economic news.
- Community: There is a social trading network for investors using this platform as well as a support forum.
Advantages
This broker is renowned for its lightning-fast trade execution. And while it is not as big a platform as MT4, it has a dedicated community of loyal users and a solid reputation.
Disadvantages
Only the basic version of this platform is free. If you want to be able to conduct backtesting, use custom indicators, or take advantage of other advanced features, you need to upgrade to paid access. At the time of this writing, that is $60 a month. If you prefer, you can pay a one-time fee of $1,099. Contrast that with the advanced features you get for free with MT4.
eSignal
- Trade Execution: Like the other top platforms we are featuring here, eSignal offers rapid and reliable execution of orders.
- Analytical Tools and charting: You can view as many as 500 symbols simultaneously and use hundreds of indicators through the App Store. There are advanced drawing tools as well as customizable studies.
- Expert Advisor/Robot Trading: Automated trading is supported by eSignal.
- Forex News: News, commentary, and research are available at the top two tiers of membership.
- Community: eSignal provides community features such as a knowledgebase, forums, and file sharing.
Advantages
eSignal takes pride in offering a huge range of trading instruments including currency pairs, indices, stocks, ETFs, and more. In terms of advanced tools and customization, they are an excellent option all around.
Disadvantages
This is another paid trading platform following a 30-day risk-free trial. There are three plans: Classic, Signature, and Elite. The Classic plan is $56 per month, while the Elite plan runs $378 per month. Some features like advanced GET technical analysis are only available at the highest tier.
ProRealTime
ProRealTime is a trading platform for forex and a variety of other instruments. There is a version you can download and install, or you can access it online through your browser on your laptop, desktop, or mobile device.
- Trade Execution: Trades execute quickly and reliably on ProRealTime.
- Analytical Tools and charting: There are well over a hundred built-in indicators and drawing tools for your charts. You also can use the code editor that comes with the program if you want to create custom indicators. You get access to more tools if you go with a premium subscription.
- Expert Advisor/Robot Trading: You can use the ProOrder automatic trading module.
- Forex News: News is built right into the platform, and if you get the Premium version, you can view up to 400 days of archived news.
- Community: The ProCommunity lets you follow the progress of traders on the platform. You can also use it if you want to manage your own network of traders.
Advantages
There are a lot of powerful features for ProRealTime, especially if you purchase a subscription.
Disadvantages
While there is a free End-of-Day version of ProRealTime, if you want real-time and intraday data, you need to pay for a subscription. As of the time of this writing, subscriptions start at $37.45 per month. That is a solid value for a high-quality platform with excellent features.
Overall Best Forex Trading Platform: MetaTrader 4
You have had a chance to compare the features, pros, and cons of some of the most popular trading platforms available.
While cTrader has come a long way, it still cannot compete with MT4 or MT5.
ProRealTime, eSignal, and NinjaTrader are all-powerful options, but they do require a subscription to access many of their advanced features. That is not the case with MT4. While you can pay for Expert Advisors and indicators for MT4, you do not need to pay for the platform itself.
Meanwhile, MT5 is a nice option if you want to trade instruments beyond currency pairs, but doesn’t add much to recommend it above MT4 otherwise.
For ease-of-use, advanced features, and extensive custom indicators, robots, and community support, it is hard to beat MetaTrader 4. There is a reason that this is the platform of choice for so many brokers and traders even after all this time.
Now you are familiar with some of the top forex trading platforms out there, and you have our overall top recommendation of MetaTrader 4. Let’s move on to talk about what you need to know about making forex deposits and withdrawals.
5. Deposit and Withdrawal

Another key consideration when choosing a forex broker is how you will move money in and out of your trading account.
Different brokers accept different methods for depositing and withdrawing funds, and also have different fees, limits and processing speeds to consider. Let’s break these factors down so you know what to look at when you are evaluating potential brokers.
Deposit and Withdrawal Methods
How do you deposit and withdraw money from your account? For your convenience, most FX brokers accept a range of different deposit and withdrawal methods. Below are some of the most common methods for adding and removing funds. Keep in mind that not every site accepts every method. Some sites may also accept methods not listed here.
- Credit or debit card. Most websites accept most major credit cards. This method offers a fast, easy, and convenient way to make a transfer.
- Bank wire transfer. It takes several days to transfer money this way, and you will usually pay a service fee. The bank charges you this, not the broker.
- Check. You can write an old-fashioned check to make a deposit into your account. This method also takes a few days to process.
- Automated clearing house (ACH). While this method can take a number of days to process, it is a secure method that can work well for large and small transfers.
- Digital wallet. You may be able to transfer money on some sites using a digital wallet service such as PayPal or Neteller.
- Cryptocurrency. You may be able to deposit and withdraw to a bitcoin wallet or another crypto wallet.
We recommend brokers that offer many methods for transfers. For example, FreshForex accepts 20 different methods.
Deposit and Withdrawal Fees
Fees may be charged on deposits or withdrawals by the broker or your bank, depending on the method you choose. For example, if you make a wire transfer, your bank will generally charge you a fee of around $25-$35.
Usually, with credit or debit card transfers, there will be no fees. But there are exceptions.
It is important to check whether a broker will be charging you fees for transfers, and if so, what they are.
That way, you can avoid brokers that are eating unnecessarily into your profits through excessive fees.
Deposit and Withdrawal Limits
For any given deposit or withdrawal method on each forex site, there may be a minimum or maximum limit to what you can transfer.
Here are a couple of examples as of the time of this writing:
- The minimum deposit on AGEA is just $1.
- The minimum deposit/withdrawal amount on VantageFX is $200 for a retail account.
- On RoboForex, the limits of the deposit for a bank transfer are €500–€100,000. The withdrawal limits are €500-€50,000. For most electronic wallets, there is a deposit limit of €10-€10,000.
- On XM, there is a minimum withdrawal of $5 using a local bank transfer and no maximum.
- On Oanda, you cannot withdraw more using a debit card than you deposited using the same card. You can only deposit up to $20,000 a month using this method.
Again, those are just a few examples. You need to look up the minimum and maximum amounts for the transfer method of your choice on the site you are thinking of trading with to know what to expect.
Deposit and Withdrawal Processing Speeds
Another way in which deposits and withdrawals can vary from broker to broker is with respect to how fast transfer requests are processed.
As we mentioned before, some payment methods are faster or slower than others. But for a single payment method, you might see differences from one site to another as well.
For example, one broker might process debit card transfers within one business day, while another might do so within 1-3 business days.
Obviously, faster is better for transfers. But even with slower transfer speeds, you can typically plan ahead and schedule your deposits and withdrawals in a way that works for you.
Questions to Ask When Researching Deposit and Withdrawal Methods Offered by Forex Brokers
We recommend that if you are considering signing up to trade with a broker, you ask yourself the following questions regarding transfers:
- What transfer method do I want to use for deposits?
- What transfer method do I want to use for withdrawals?
- On this site, if I want to make a withdrawal using method X, do I also need to use method X to make my deposit? Will that work for me?
- Is the processing time for the transfer method I want to use sufficient for me for both deposits and withdrawals?
- Are there fees for deposit? What about withdrawal? Are they reasonable?
- What is the minimum deposit amount? Can I afford it?
- How much can I withdraw at one time using the method of my choice? Will that ceiling be appropriate for me?
It should be fast, affordable, and convenient for you to transfer money to or from your forex account.
If you are satisfied with the methods and policies at the site you are thinking of joining, it may be a good fit for you.
Now you know more about making deposits and withdrawals on forex websites. Read on to the next section to learn what you need to know about opening an account on a forex website.
6. Account Opening

We have talked about different types of deposit and withdrawal methods for trading forex. But before you can deposit money into an FX account, you first need to open one. So, how do you do that?
The exact process of opening an account depends on the specific broker you are using. In this section, we will go over the basic steps you can expect when registering to trade at most sites.
Criteria of Account Opening
As we review each step, we will talk about some relevant considerations that may impact your choice of a broker. These include:
- Overall speed and ease of account opening
- Documentation required
- Types of accounts
- Approval speed
- Minimum funds to open an account
- Available base currencies
- Maximum leverage available
- Languages available
- Regions accepted
Questions about Account Opening
You can find out about a lot of these differences between brokers before you ever start the account opening process. So, we recommend checking the FAQs of brokers you are considering before you start the account setup process.
You also can check forex forums and social media sites to view real feedback from customers about the ease of the account opening process and the speed of verification.
Ask yourself the following questions while conducting your research:
- What is your preferred way to submit identity verification documents?
- How much do you want to deposit to start with?
- What lot size do you want to trade?
- Do you need a special type of account, like an Islamic account?
- What base currency do you want for your account?
- Are you in a region where not all brokers are likely to accept you?
- How soon do you want to start trading? How fast do you want approval to be?
Based on your answers to those questions, you can choose a broker that will allow you to open an account that fits your requirements and hopefully will encounter no surprises along the way.
Now, let’s go over the process of opening a forex account, noting where you may encounter divergences between different trading sites.
How to Open an Account with a Forex Broker
Click on “Register.”
To get started on any forex site, you will click on a button to open an account. It might say “Register” or “Sign Up” or “Open an Account” or something similar.
Provide your basic information.
The next step will usually be to provide your basic information to open an account. That means your email address and choosing a password, at the minimum. You might be asked for some other basic information as well.
At this point, you typically will have to check a box saying that you agree to the terms and conditions.
Check your email.
Usually, you will either be sent a pin number that you will need to type in to confirm your email address, or you will receive an auto-generated password in your inbox if you were not asked to enter a password when you registered.
Check your email for the information you need, and enter it on the page where you are asked to do so.
Log in.
If the site does not automatically log you in, log in manually.
Create a trading account.
Once you are logged in, you will need to open an account to use for trading. There may be several types of accounts available, depending on the broker. Some options might include:
- Real account
- Demo account
- Islamic account
Select the type of account you want. Choose your preferred leverage and currency, and answer any other questions you are asked.
Don’t see the type of account you want? You may need to choose another broker.
Likewise, if you require more leverage than a particular broker offers, you will need to pick one that offers higher maximum leverage.
Most major FX sites will accept major currencies like USD, EUR, and GBP.
If your preferred currency is unavailable, that does not mean you cannot trade on a site. It just means you will need to convert your funds into one of the acceptable currencies when making a deposit.
Note that real accounts fall into the following categories:
- Standard
- Mini
- Micro
Each of these types of accounts has a different lot size.
- Micro lot = 1,000 units of your account currency
- Mini lot = 10,000 units of your account currency
- Standard lot = 100,000 units of your account currency
You need to choose a lot size and corresponding account type that is appropriate for your money management plan. The larger the lot size, the higher the risk.
If a broker does not offer the lot size you need, once more, you will need to look elsewhere.
Agree to further terms and conditions as required. Once you have filled in all the details requested, you should receive an account number and a password for that specific account.
Provide detailed profile information.
The site will now ask you for some more details. For example, you will need to provide your real phone number and address. It is important to make sure this information is accurate, or you could lose your account later.
Indeed, if a particular broker does not accept customers from your region, you should choose one that does.
Otherwise, you will not be able to complete the identity verification process.
You also will need to answer questions about your employment status and your financial situation. Responsible forex sites want to encourage only those with the means to trade forex to do so. You also may need to answer questions about your experience with FX.
Some sites ask more questions than others, but it should only take you a few minutes to answer them all in any case.
In fact, the entire account opening process up to this point should take you around 10 minutes on the majority of sites.
Submit your documents.
Before you can deposit or withdraw money from a trading account, the site needs to know that you are who you claim to be. This is a policy called “Know Your Customer,” or “KYC.” So, you will need to submit your proof of identity and proof of residence at this stage.
This is why it is important to provide accurate information when you sign up for your account with respect to your name, address, and so forth. If there is a mismatch between the info you provide and the info in your documents, it will cause problems.
KYC can be easier on some forex sites than others.
- Some sites may accept a wider range of documents to prove your identity and residence than others.
- Some brokers may allow a wider range of file formats than others.
- The submission process itself may be facilitated by certain sites. They may, for instance, provide helpful diagrams, or they might have an app that snaps a photo of your document through your device.
- Different brokers may offer different means of submitting documents (i.e. email, fax, through the site itself, etc.).
- FX sites can vary in how stringent they are about clarity, legibility, etc. Those that are stricter may require you to resubmit documents if they spot a problem.
Forex sites often aim to process documents and verify accounts within 24 hours, but some sites may take longer or shorter timeframes to complete the process. In some cases, the process may take as little as an hour.
Make your deposit.
After the verification process is complete and the broker finalizes everything with your account, you can make your deposit. Processing times can vary; read more about this in our section on deposits and withdrawals.
It is important to note that the minimum deposit size can vary dramatically between brokers, so choose a broker that allows you to open an account size that is suitable for your needs.
Start trading.
Once your money is in your account, you will be able to trade forex. Read on to learn about some of the markets and products available for you to trade online.
7. Markets and Products

Now that we have talked about opening an account with a forex broker, let’s talk about another area where brokers may differ, and that is with respect to markets and products.
Markets
Each broker you encounter will offer a different selection of markets. These are the assets that are available to trade.
Some types of assets are very common and are pretty much ubiquitously available among brokers. These include, for example, major currency pairs like GBP/JPY or EUR/USD.
Other financial instruments may be more obscure, and may not be available to trade everywhere.
Here are some of the different categories of assets you can find to trade on forex websites:
- Currency pairs: You are probably signing up for a forex account mainly to trade foreign exchange currency pairs. Examples include EUR/USD, GBP/USD, USD/JPY, and so forth. Again, major pairs like these are almost universally available. But some sites might offer more exotic pairs like USD/MXN or EUR/HUF. Exotic pairs tend to feature more whipsaws and unpredictability, but some strategies are built around them.
- Cryptocurrencies: On some websites, you can trade crypto pairs as well, for instance, ETHUSD or LTCUSD.
- Commodities: Want to try your hand at trading commodities? Precious metals, oil, and soft commodities are commonly available to trade on FX sites. Some examples of soft commodities include orange juice, cotton, cocoa, and coffee.
- Indices: Some brokers offer indices to trade such as ND, DJ, S&P500, and others.
- Equities: If you want to trade equities, you will find this market available at some forex brokers. Examples of equities include “.BAC.N”, “.CVX.N”, and “.MA.N”.
- Futures: Futures contracts may be available to trade on a number of different types of assets, including commodities and indices.
- CFDs: Some forex brokers allow you to trade contracts for difference (CFDs) on stocks, commodities, and other assets.
Importance of the Markets
How important is it for a broker to offer a wide range of markets? Well, that really depends on your trading plans.
As a selection criterion, it might be essential or insignificant, depending on what you want to do.
A variety of assets is nice to see since a lot of what you learn trading one financial instrument might carry over to trading another.
Some systems are versatile enough that you can use them to trade a variety of assets once you make some adaptations.
So, you might plan to do just that to expand your trading opportunities. This might be particularly helpful if you are trading on lower timeframes, and need more entries than you are likely to get with just your basic set of currency pairs.
On the other hand, you might be planning on just trading one or two currency pairs for the indefinite future—depending on your strategy, sometimes that is enough to bring in steady revenue. There is nothing wrong with that, in which case you might not care if there are hundreds of exotic assets available.
Products
Along with a range of different trading markets, forex brokers also may differ in terms of the selection of trading products they offer.
Basic currency trading is one type of trading product. Here are some others you might encounter:
- Binary options: With these simple trading products, you predict whether the price of a given asset will be above or below a certain threshold at the expiry time.
- Social trading/copy trading: With this feature, you can see how other investors are trading for one or more assets, and then duplicate those trades in your own account. On some sites, you can do this manually, while on others you can do it automatically. You might also be able to choose whether to manually copy trades or auto-copy trades.
- PAMM: This stands for “percentage allocation management module” or “percentage allocation money management.” If you do not want to plan and execute your own trades, you can allow a money manager to do it on your behalf through PAMM trading.
- Trading signals. Need help spotting opportunities to enter trades? Sign up for trading signals. While you can get free or paid trading signals through third parties, some forex brokers offer them as part of one or more account tiers.
- Robots: With a robot, or “automated trading,” you can have a bot place trades for you. Sometimes a robot may also be called an “advisor.” The robot will follow a programmed set of rules for recognizing and executing trades. Free robots may be available through your platform or broker, or you may be able to purchase them. You also might be able to build your own.
Importance of the Products
Again, how important are these products really depend on the approach you want to take with trading forex.
If you never want to trade binary options, for instance, it does not matter if they are available or not. But if you really want to try this product out, then you should make sure it is available at the broker you are interested in.
On the whole, robots, trading signals, PAMM, and social trading are all very useful features. They can take a lot of work off your plate and save you time so you can focus on other aspects of your trading when you need to. And even if you do not want to rely on them, you can still use them as additional sources of insights when coming up with your own manual entries and exits.
Now you know about some of the different types of markets and products you may find when selecting a forex broker.
Make sure you sign up for an account on a site that offers the assets you want to trade and the products you need to succeed.
Read on to our next section to learn about the various educational resources that forex brokers provide to traders.
8. Education

In our last section, we went over the different markets and trading products that forex brokers may offer. In this section, we will talk about the educational resources they may make available to you.
Why Are Educational Resources Important for Forex Traders?
Every forex trader is somewhere along a learning curve. This is true whether you are brand new to FX and still learning the basics, or whether you have been trading currencies for years now.
If you are reading this article to help you choose an FX broker, we are guessing you probably are still quite new to forex. You are probably picking your first broker, or maybe your second if the first did not work out.
That means that you still have lots to learn about:
- Forex trading in general
- Strategies and methods for trading FX
- Money management
- Trader psychology
The more educational resources your broker offers you, the easier it will be for you to pick up the knowledge and skills you need to advance your trading career.
Types of Educational Materials
Not all brokers offer the same types of educational resources, nor the same quality of materials. Here are some of the different types of resources you may encounter.
Educational Resources That Introduce You to Trading on the Site
- FAQ: One of the most basic educational resources that almost every FX site includes is an FAQ. This page will teach you about the broker itself and its features.
- Live onboarding sessions: Some forex brokers offer live sessions to new traders to help them learn their way around their platforms, products, and features. During these sessions, you have an opportunity to ask any questions you might have, making it easy to get started trading.
- Platform tutorials: Brokers may offer tutorials you can read or watch to learn how to use their proprietary platforms or third party platforms they work with.
Educational Materials That Teach You How to Trade Forex
- Articles: A broker may maintain a database of articles or a blog with regular posts. Either way, these resources can teach you more about forex trading through the written word as well as screenshots. Topics could include how to use various trading indicators, how to interpret financial reports, tips for managing your money, and more.
- Financial news. Stay current on the latest events in the financial world. Brokers may simply offer the news for your interpretation or might offer their own analysis.
- Videos: Forex brokers may have a selection of videos available for you to teach you trading concepts.
- Webinars: If you want to see forex strategies in action, check to see if a broker hosts webinars. When you tune in, you can watch live demonstrations of different trading methods and tools. You will have a chance to ask questions as well and learn directly from a trading expert.
- Classes and coaching: There are brokers that go above and beyond to offer full courses on forex trading. These may include hours of video lessons as well as live mentorship sessions from a trading coach.
What if My Broker does not offer these Educational materials?
Since not every broker offers all of these resources, be sure to check whether the educational materials you are looking for are available on the site you are thinking of joining.
Should they be a make-or-break selection criterion? Probably not. There are other resources out there you can use, and other criteria such as available markets and trading tools and features should probably take a higher priority.
Nevertheless, it saves you time if you already have a lot of excellent resources waiting for you on a trading site.
Plus, it says something positive about the broker. If they are offering you educational materials, they are showing that they care about your success. They also are encouraging you to trade responsibly.
What Makes for a Quality Resource?
We have talked about the different types of educational materials that brokers may offer. But we have not yet talked about differences in the quality of resources.
Two forex brokers might both offer a selection of trading videos, for example—but the quality difference between them might be enormous.
Quality educational materials:
- Are clearly presented or well-written, and are available in your preferred language.
- Provide thorough explanations of topics, not just images (i.e. a video should include a helpful narrative component, not just someone circling formations or adding indicators in silence).
- Cover more than just beginner topics. The more intermediate and advanced content available, the better.
- Are not sales pitches in disguise. You shouldn’t run into this on any well-established forex sites, but we have seen it on some smaller sites. Educational materials should teach you how to trade, not try to sell you on opening an account.
So, don’t just hover your mouse over the menu to look at the drop-downs and note that a “video library” or “articles” are available. Click on each, and see whether the selection is high in quality or not.
Consider Your Learning Style As Well When Making Your Selection
One more thing worth mentioning is that no one type of educational resource is “best”—it really comes down to your learning style.
Some people learn best by reading, while others learn more from looking at pictures or watching videos. Still, others advance their knowledge best when they are watching a live demonstration during a webinar.
So, think about how you learn best. If you learn most effectively from reading articles, a site that offers nothing but videos will not fulfill your educational needs.
Likewise, if you learn most effectively through videos or webinars, a huge database of articles will not be nearly as helpful to you as those other resources.
Now you know how to compare the educational materials that various FX brokers offer. Let’s press on to what to look for in terms of customer service.
9. Customer Service

You now know what to look for in terms of quality educational resources when selecting a forex broker. But here is something you may not have thought about yet: customer service.
Why is Customer Service Important When Choosing a Forex Broker?
Put simply, customer service is more important when choosing a forex broker than it likely is with respect to the majority of the products or services you use.
Why? Because you are trusting the broker with your hard-earned cash. If you need an answer fast or you need help with an urgent issue, it isn’t just going to inconvenience you if the service is unresponsive or unhelpful. It is literally going to cost you. And in some situations, it could end up costing you a lot of money.
You might think that there would not be a lot of variation in the customer service experience from one broker to the next, but divergences can be dramatic.
When you check into customer support options for brokers you are considering opening accounts with, you should consider both the accessibility and quality of service. Let’s discuss each of these in turn.
Accessing Customer Service
Different brokers may offer you different means of getting in contact with the customer support team.
Some brokers may give you many channels of access, while others may confine you to just a few.
Here are different ways of contacting customer service you may encounter along with some of their advantages and disadvantages.
Telephone
With this method of contact, you can pick up your phone and call a customer service agent to discuss your questions or concerns.
Sometimes it is hard to beat being able to talk to someone with your voice and hear theirs. It can help establish a stronger rapport and get someone to take an issue seriously.
On the downside, you cannot save a log of a phone call for later reference. Also, if there are issues with the clarity of your connection, you might have trouble understanding each other.
Some FX sites may offer a single telephone number for all calls. Others may provide local numbers. Check to see if there is a phone number for your country if that is important to you.
Live Chat
Live chat is an alternative to the telephone that allows you to speak to an agent in real-time by typing messages on your device.
While some people prefer hearing a human voice, others may communicate more easily in text and/or find it more convenient.
Plus, with live chat, you can save a log of your conversations, which might be useful to reference later.
Many forex websites offer one or more email addresses for customer support inquiries.
While emailing customer support at a forex website will not get you real-time support, it may still get you a fast reply, depending on how quickly the site tends to respond to its emails.
If there are multiple email addresses, it might mean a quicker response since your email will be routed to the best person automatically.
Even though real-time support may get you the most rapid resolution, email can be more convenient when you do not have the time to sit on the phone or live chat with someone.
You also will have records of all of your emails and the customer support team’s responses if you need them.
Web Form
This method is a lot like sending an email, except that you type your message into a form on the website and input some basic information, and then wait for a response.
The downside over an email address is that you do not have a copy of your original sent message unless you remember to manually save one before you hit “send” on the website form.
Ticketing System
Ticketing systems work pretty much the same way web forms do, except that they generally will require you to be logged in.
A webform may be accessible to the general public, but a ticketing system is only for customers.
Forum
There may be a support forum for a forex website if that site has an associated community.
On that forum, you may receive support from customer service representatives, tech support staff, other traders, or all three.
This is a useful feature in general, but we advise caution if you see a site that does not offer many other support options besides a community.
Such a site may be trying to foist some of the work of customer service off onto the community.
It should not be the job of other traders to help you; it should be the job of the forex broker.
Support you receive through a public channel like this may also be more impersonal than support you receive through email, live chat, or over the phone.
Be Sure to Check the Support Hours
Regardless of the method of contact that you plan to use, you should check the support hours available.
Some forex brokers might offer customer service 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. Others might restrict their customer service hours to 5 days a week. Still, others might not offer round-the-clock service, but most do since forex customers come from all over the world.
There may also be service hour differences between different methods for the same broker.
For example, a broker could offer 24/5 support via live chat but only look at tickets between 7 in the morning and 4 in the afternoon.
There are many excellent brokers that do not offer 24/7 customer service at all. But all other things being equal, 24/7 service is best.
What Languages is Support Available In?
Just as there are differences in support hours between forex brokers, there also can be differences in languages.
Some forex sites might just offer support in English, while others could offer support in several or more languages.
If you need support in your native language, make sure that it is available.
How Do You Evaluate the Quality of the Service Team Itself?
We have now talked about the accessibility of customer service with respect to different means, languages, and hours.
But you should also consider testing the quality of the support itself.
How can you do that? Think of a question, especially one not answered in the FAQ, and simply contact support via the means you prefer and ask it.
Then, check to see if you are satisfied with how the staff addresses your question or concern.
Good Customer Service Agents Should:
- Not make you wait forever to talk to someone. Check the phone or live chat at a few random times on random days to get a feel for what standard wait times are like. You do not want to be waiting around for hours to talk to someone about an urgent issue.
- Reply promptly to you when they are available. It can be frustrating to talk to agents who take forever to type a sentence (this applies to the live chat line, specifically).
- Be knowledgeable and thorough. Good customer support agents should be well-versed in forex and what their company offers in terms of markets, tools, and more. They should not struggle to answer simple questions. Those answers should be at the ready because they should know them inside and out.
- Go the extra mile to get you the answers you need. If you ask a question that an agent does not know the answer to immediately, they should be willing to go and hunt it down for you, even if that takes some time. When they get back to you, their reply should be thorough.
- Be friendly. You should feel welcome and appreciated as a customer or potential customer at a forex website.
- Make you feel comfortable. You should instinctually feel like you are dealing with someone you can trust with your money.
Good Customer Service Agents Should Not:
- Dance around questions. If a customer service agent is dodging a question (especially a regulatory one), that is a bad sign. It might mean that the company you are thinking of trading with is not trustworthy.
- Not know the answers (or take the time to find them). You do not want to be dealing with customer service agents who do not know what they are doing if you have a problem involving your money, and you especially do not want to be dealing with lazy ones.
- Try to hurry you along. Your questions or concerns are important. No customer service agent should ever be impatient or dismissing your issues.
- Hard sell you. If you do not yet have an account while you are testing customer support, there is a good chance an agent will try to convince you to open one. There is nothing wrong with this, but if the sell is particularly aggressive, that is not a positive sign. The company should be urging responsible trading.
The quality of customer support at a forex broker determines much about the quality of your experience as a trader and it tells you how much the broker cares about that experience.
Now you are ready to evaluate customer service when choosing a broker to trade forex with. In our next section, we will talk about research tools.
10. Research

When it comes to actually trade forex, you will probably search for setups using fundamental analysis, technical analysis, or price action.
There is a degree of research involved with this, especially if you are going the fundamental route.
Some forex brokers offer more resources than others to assist you with researching trade ideas.
Let’s take a look at a few different categories of research tools you might find.
Trading Ideas
If you do not have your own system you strictly follow 100% of the time, you might be interested in trade setups that other investors recommend.
On some forex sites, you will find a section for trade ideas. Sometimes these will be provided by an in-house team. Other times, the broker might source them from third-party analysts.
The trade ideas could involve technical or fundamental analysis or price action.
If a site only posts a few trade ideas now and again, you might find them in the blog or news section in individual posts.
Brokers that share a lot of trade ideas may have a more organized way of presenting their idea feed and might sort them by financial instrument to make it easy to find what you are looking for.
News Feeds
If you like to use fundamental analysis, news feeds that tell you what is going on with economic markets can help you to come up with ideas for your trades.
Reading up on the markets also can help you get a broad view of what you can expect in the near future in terms of volatility, trade volume, and so forth.
Ideally, there will be charts in the news feed, but some feeds do not include them.
Also, you may be able to set up alerts for specific types of news items. You can have the alerts sent to your email address or text to your phone.
Fundamental Data
Interested in trading stocks? Forex brokers that offer stock trading may also offer fundamental data.
This data might include company profiles, valuation ratios, price performance, historic growth, financial statements, and so forth.
Interactive Charting Tools
If you are coming up with your own trade setups, you will need to choose a broker that allows you to use a platform with a rich suite of charting tools.
These include drawing tools and technical indicators. By plotting them on your chart, you can identify potential trends forming, reversals, and other opportunities.
You will find much bigger selections of charting tools on some platforms than on others. Platforms like MT4 also allow you to load in custom indicators or even make your own.
Economic Calendar
If you are trading using fundamental analysis, you will definitely want to have access to a handy economic calendar. Most forex brokers do provide one.
The economic calendar alerts you to upcoming financial events, including dates, times, and forecasts for each item.
Even if you are not trading with fundamental analysis, you might want to keep an eye on the economic calendar, as the price can become more volatile when reports come out or other major financial events take place (there are differing schools of thought on this).
Social Trading
Finally, one more feature that can give you ideas for your trades is social trading. With social trading, you can follow the trades that other investors are making through your broker.
If you find a trader who seems to know what they are doing, copying their trades (social trading is also called “copy trading”) might help you to succeed as well.
You might need to do this manually, or you may be able to automate it, depending on the platform you are using.
Pick a Broker That Offers the Tools You Need
Now you know what types of research tools you might find at different forex brokers. You do not necessarily need this full selection of tools, but you do need to think about how you plan to trade and choose a broker that offers you the tools you require.
So, for example, if you are a fundamental analysis trader, it would be important to choose a broker that offers an economic calendar, a news feed, and perhaps fundamental data.
If you are a technical analysis or price action trader, you will want a solid selection of interactive charting tools, but having access to a news feed or economic calendar might not be as important to you.
If you want to invest, but you do not want to plan your own trades, you might consider a broker that offers ongoing trade ideas as well as social trading.
Plan to come up with all of your own trade setups? Social trading and trade ideas might not matter to you as much.
11. Forex Promotions and Bonuses

For a lot of new forex traders, bonuses and promotions are a compelling draw to sign up on a broker site. What do you need to know about forex promos, and how should they influence your choice of a broker?
Types of Forex Bonuses and Promotions
You may encounter a number of different types of bonuses and promotions when you are checking out different forex brokers. Here are some common ones:
- Welcome deposit bonus: When you make your first deposit into a forex account, you may receive a welcome bonus based on the amount of your deposit. For example, you might receive a 20% welcome bonus of up to $5,000. Or you might receive a 30% welcome bonus up to $3,000, or so on. Different sites offer different match percentages and maximums.
- No deposit bonus: This type of bonus is similar to a welcome deposit bonus, except that no deposit is required. All you need to do in order to claim it is to open a new account on a forex site. The broker will then credit your account with the no deposit bonus.
- Reload bonus: This is similar to a welcome bonus, except that you do not need to be making your initial deposit in order to claim it. As a returning customer, you can qualify for a match on your next deposit.
VIP Programs
Along with the types of forex bonuses listed above, some websites offer VIP programs. These sometimes take the form of rewards programs that you can apply for or be invited to based on your trading volume or other factors.
Alternately, the VIP “program” could simply be an account tier. Instead of signing up for a basic account, for example, you might sign up for a “VIP account,” “advanced account,” or so forth.
Normally to open this type of account, you need to be able to make a larger deposit. But once you do, you will have access to all the features and benefits that come with that account.
In some cases, that can include promotional rewards such as lower commissions or even cash rebates. In order to maintain your account status, you will need to meet a minimum trading volume.
Forex Contests
Some forex brokers also run contests. These may include live contests and/or demo contests.
Contests typically run at monthly intervals. You compete against other traders, and if you win, you receive a bonus credited to your account.
Rollover requirements may apply. Whether or not it is possible to withdraw the bonus depends on the terms and conditions for that particular contest.
Forex Bonus and Promotion Terms and Conditions
Along with the different types of bonuses that forex brokers offer, you should pay attention to their terms and conditions. These may differ significantly from one site to another. Some sites may offer friendlier terms than others.
Countries
You should not automatically assume that every bonus you see will be available to you regardless of your region.
Some forex brokers restrict their promotions to specific countries while excluding others. So, before you attempt to sign up on a site to claim a bonus, you should make sure that it will be available to you based on your location.
Types of Accounts
Just as some forex brokers restrict their promotional offers to users from certain countries, they may also restrict them to users with specific types of accounts.
Before you get excited to claim a promotion, check whether you will be able to claim it with the type of account you plan to open.
Rollover
It is common for forex bonuses to come with rollover requirements, also known as turnover requirements.
In order to withdraw the bonus and/or winnings, you have to meet that requirement. It will be expressed like x10, x20, x30, x40, x50, or so forth.
This number represents how many times you need to “turn over” the funds in your account to meet the requirement.
So, for example, let’s say that you claim a bonus of $100 after you deposit $300. You now have a total of $400 in your account that you can use for trading.
Before you claimed this welcome bonus, you noticed in the terms and conditions that it included a x20 rollover requirement.
Reading the terms and conditions more closely, you saw that you need to turn over the amount of the bonus plus your own funds 20 times to meet the requirement.
So, that would be $400 x 20 = $8,000.
Only after you achieve that turnover are you able to withdraw the bonus and the money you have won with it.
Obviously, the lower the rollover requirement is, the better.
So, if you are considering the quality of bonus offers at various sites as a determining factor for whether or not to join, be on the lookout not only for large bonuses but also for small rollover requirements.
Can You Withdraw the Bonus?
It is pretty common not to be able to withdraw a bonus credited to your account at all, even after meeting the rollover requirements. However, you are often allowed to withdraw the profits you have made from trading with the bonus.
But you may sometimes find forex brokers that allow you to withdraw the bonus as well after you meet the turnover requirements.
Consequences of Not Meeting Rollover Requirements
Another of the terms and conditions you should compare when you are looking at forex bonus offers between brokers is what will happen if you try to withdraw before you achieve the turnover required.
Will doing so just result in not being able to make a withdrawal? Or will it result in you forfeiting the bonus? What about your winnings?
The less restrictive bonus terms are, the better. But the most important thing is just to be aware of the terms for any given promotion before you accept it.
That way, you will not make a mistake that will result in an unwelcome surprise.
Always Read the Terms and Conditions Before Accepting a Forex Promotion
We cannot emphasize enough how important it is to read the terms and conditions carefully before you accept any forex bonus or promotion.
Not only should you do this to compare bonus offers between different brokers you are considering, but also to educate yourself about what you can expect if you accept a promotion.
Far too many novice traders do not understand how rollover requirements work. They also may be surprised to discover that a bonus is not always available to withdraw even after meeting turnover requirements.
If you do not acquaint yourself with the terms and conditions for a bonus and are caught off guard, you may feel that you have been ripped off.
But this will not happen if you take the time to read the terms and conditions for forex bonuses carefully before accepting them.
How Important Should Bonuses and Promotions Be When Deciding Whether to Open a Forex Account?
It is reasonable to consider the values of various forex promotions and bonuses before you choose a broker. But it should not necessarily be one of your top considerations.
Ultimately, features and factors such as deposit and withdrawal methods and processing times, fees and commissions, order execution, charting features, and regulatory status are all going to have a much bigger impact on your life as a trader.
So, we recommend choosing primarily based on practical considerations such as those, with bonuses and promotions as a secondary consideration.
12. Supported Trading Styles

We have just about reached the end of our guide to choosing a forex broker. But before we wrap up this guide, we want to take a few minutes to discuss how your trading style might impact your choice of a forex broker.
Depending on the approach you take to forex trading, you may benefit from specific features and tools.
A broker that offers those features and tools may be an ideal fit for you. One that does not may not offer you what you need to effectively utilize your strategies to profit.
What is Your Trading Style?
Following are some possible ways you might describe your trading style:
- Position trader
- Swing trader
- Intraday trader
- Interday trader
- Scalper
- Technical trader
- Price action trader
- Fundamental trader
- Hedge trader
One or more of these terms could apply to you depending on your approach.
Following, we will go over some important considerations for some of these trading styles and how they might impact your broker choice.
Timeframe Considerations
Long-Term Traders
Are you a long-term trader who will be holding your positions over the course of weeks, months, or even years to profit off of long-term trends?
If so, you will want to pay close attention to the rollover fee that a broker will charge you. This fee may also be called the “swap rate.”
Part of what you are charged is simply the differential in interest rates for your pair.
But your broker may also tack on an administrative fee when your position is open overnight.
The longer you have a trade open, the more your overnight fees can start to eat into your profits.
So, as a position trader, you should look for a forex broker that is not going to bleed you dry with overnight fees.
Chances are good that you use economic data while planning and monitoring your long-term trades. You also may make use of charting tools like moving averages.
Ideally, your broker will provide you with useful tools and resources that help you manage your position traits.
Scalpers
On the polar end of the scale when it comes to timeframes are scalpers. Instead of holding a position for weeks, days, or even hours, as a scalper, you close your positions within minutes or seconds.
Naturally, overnight fees are not of any concern to you if this is how you conduct the majority of your trading.
But higher spreads and commissions may eat into your profits rapidly, as you probably are placing numerous trades each day.
So, it is very important to look for low spreads and/or commissions when choosing a broker.
Also, since you will be entering and exiting trades sometimes within seconds, rapid execution is crucial.
Another important consideration is whether a particular broker is going to allow you to scalp on a regular basis at all.
Dealing desk (DD) brokers (“market makers”) sometimes ban scalping.
You can avoid this problem by choosing a no dealing desk (NDD) broker.
This can be either a straight-through processing (STP) or electronic communication network (ECN) broker.
So, this may be one of the first things you look up about any broker you are considering.
Interday Traders
What about traders who open positions for several days at a time? If that describes you, you are an interday trader.
You will want to consider overnight fees when you are investigating potential brokers, but spreads and commissions will be important to you as well since you will be placing fairly frequent trades.
Another consideration with respect to interday trading is what time of the day you will be opening and closing positions.
If your trading method and the pairs you are trading result in a lot of overnight activity, it is important that you choose a broker that offers a platform that lets you set up alerts. Otherwise, you will miss opportunities while you are sleeping.
Method Considerations
Fundamental Traders
If you use fundamental analysis as part of your trading method, look for a broker that provides you with resources that help to support that style of trading.
Examples might include news feeds, fundamental data, and an economic calendar.
Also, do you plan to trade when reports are released? Times like this tend to result in high volatility, so a broker with low slippage would be ideal.
Technical Analysis Traders
If you trade based on technical analysis, the most important tools for you will be drawing tools and indicators.
In case of that, you will be using a broker’s proprietary platform, be sure to check to make sure it has what you will need or allows you to import it or build it.
If you will be using a third-party platform like MT4, there should be no issues.
Also, consider the overall appearance and quality of the charts. They need to be easy to read, and you should be able to customize them so that you can see what is going on in the market with minimal effort.
Price Action Traders
If you trade using price action, the most important consideration is the quality of the charts, as just discussed.
You likely use drawing tools for context, and maybe you use some indicators as well. Make sure that whatever you need to put on your charts is available to you.
Other Trading Style Considerations
Hedging
Is hedging among your forex trading strategies? If so, you need to find a broker that allows you to hedge, as some brokers ban this practice.
If you are wondering why some forex brokers will not allow you to hedge, it has to do with NFA Compliance Rule 2-43b.
This is a US law that has been around since 2009.
Under this regulation, forex dealer members (FDM) and retail foreign exchange dealers (RFED) must ban hedging and need to use a first-in-first-out (FIFO) basis to offset positions.
So, if you want to hedge, choose a forex broker that lets you.
Robots, Signals, and Social Trading
Finally, it may be your trading style to plan all of your trades yourself, but it might not be. Some traders prefer to utilize tools such as robots, signals, and social trading to save time and effort.
With these tools, you can use setups for trades identified by other traders or software.
Automated trading may also include the software capability to place entries and exits on your behalf.
Some trading platforms support these features while some do not.
If you are using a proprietary platform, check to see if it supports signals, social trading, and robots if you want to use them.
Money Management
One more consideration with respect to your trading style and choosing a forex broker is how you plan to manage your money.
If, for instance, you want to trade with high leverage, you will need to find a broker that offers the level of leverage you are looking for.
On the other hand, perhaps you want to keep your trades very small, perhaps around 2% of your account, and you do not have a lot of money to deposit, to begin with.
If that is your situation, you should look for a broker that offers very small or even custom lot sizes so that you can stick with your strict money management plan.
Your Broker Should Support Your Trading Style
We have now gone over a wide range of important considerations for choosing a forex broker based on how you will trade.
If a broker does not offer the features and flexibility you need for your trading style, you are not going to be successful.
But if you find a broker that can support your trading style with sophisticated features and low costs, that broker will empower you to succeed.
Discover Top Forex Brokers Now
Congrats! You have now finished reading our guide on how to choose a forex broker.
You have learned about fees, security, regulation, trading platforms and tools, deposits and withdrawals, markets and products, and more.
Not only have you learned how to evaluate the values of these features, but you also have discovered how to do so in the context of your individual trading style, taking into account your financial resources and goals.
Ready to find the forex broker that is right for you? Check out our in-depth reviews to get started.


